Table of Contents
Zonal Councils
Zonal councils are Indian government bodies that help with development and coordination among states. They monitor various policies and programs in states and make suggestions for better growth. India has five zones, and each state belongs to one of them.
The Union Home Minister is the chairperson of all zones and makes decisions for state development. There are 28 states and 8 union territories in these five zones, which were reorganized in 2019 after changes to Article 370 regarding Jammu and Kashmir. The Zonal Councils are covered under the Indian Polity and Governance section of the UPSC Syllabus. Students can also go for the UPSC Mock Test to get more accuracy in their preparation.
Zonal Councils History
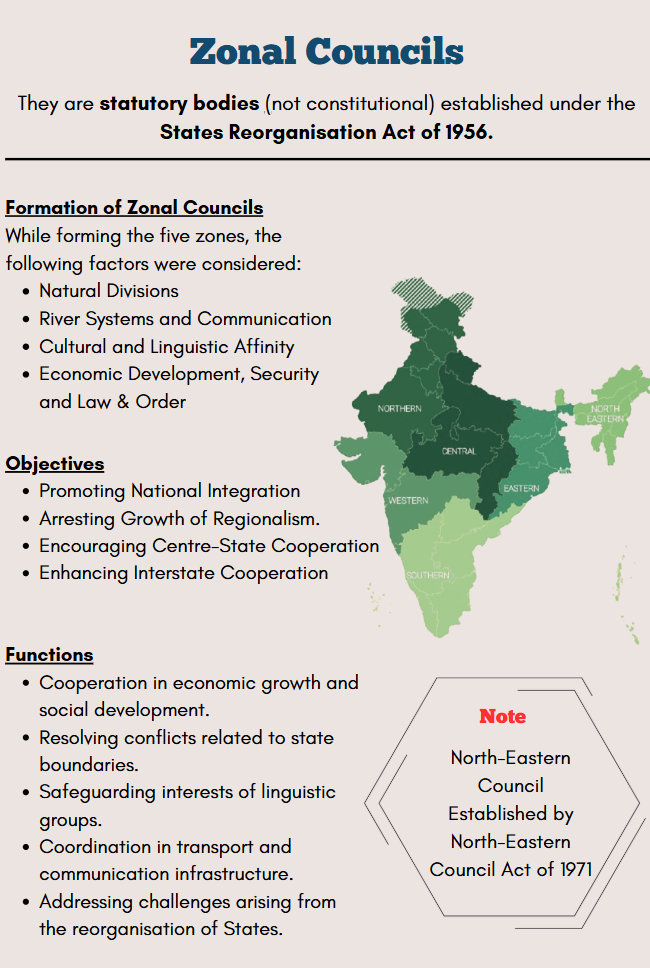
Zonal Councils are advisory bodies set up by the States Reorganisation Act of 1956, dividing India into five zones: Northern, Central, Eastern, Western, and Southern. They consider factors like natural divisions, river systems, cultural ties, and economic needs when forming these zones. Also, the North-Eastern Council was established by the North-Eastern Council Act of 1971, including members from states like Assam and Manipur.
Zonal Councils Composition
The States Reorganization Act of 1956 (Part III) authorized the establishment of five Zonal Councils, as proposed by Prime Minister Jawaharlal Lal Nehru. Each zone of the zonal council is currently constituted as follows:
| Council | Description |
| The Northern Zonal Council | Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, the Union Territory of Chandigarh, and the National Capital Territory of Delhi are included in it. |
| The Eastern Zonal Council | The States of Bihar, Sikkim, West Bengal, Jharkhand, and Orissa are comprised of it. |
| The Central Zonal Council | It comprises the States of Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Uttrakhand. |
| The Western Zonal Council | It includes Goa, Dadra & Nagar Haveli, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and the union territories of Daman & Diu and Daman & Diu. |
| The Southern Zonal Council | Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and the Union Territory of Puducherry are included in it. |
Objectives of Zonal Councils
- Promote national integration.
- Reduce regionalism and linguistic divisions.
- Foster cooperation between the Centre and states.
- Support effective development project execution.
Organizational Structure of Zonal Councils
| Structure |
|
Chairman
The Union Home Minister presides over each subdivision of the zonal council.
Vice-chairman
A Chief Minister, along with the other two Ministers, are chosen by the Governor to serve as the vice-chairmen of each State and two of the Union Territories (UTs) that are part of the zones. For a period of one year at a time, it is carried out in an ongoing manner.
Advisors
These are the people who have been put forth for each zonal council subdivision by the Planning Commission, Chief Secretaries or any other officer.
Zonal Councils Functions
Each Zonal Council acts as an advisory group that can discuss any issues important to the states in that council or between the states and the central government. It provides advice to both the Central Government and the state governments on the best actions to take regarding these issues. A Zonal Council, for instance, may talk about and recommend things like:
- Any topic in the sphere of economic and social planning that is of general interest;
- Any issue including disagreements over borders, linguistic minorities, or interstate transportation;
- Any issue relating to or resulting from the States’ reorganization under the States Reorganization Act.
Zonal Councils UPSC
The first Prime Minister of India, Pandit Jawahar Lal Nehru, proposed the concept of establishing a zonal council in 1956. It was tossed out during the discussions that followed the release of the States Reorganization Commission’s final report. The States Reorganization Act of 1956 (Part III) led to the establishment of five zone councils.
Every zonal council is regarded as a consultative body. The formed zonal council’s organizational structure consists of a chairman, vice-chairman, members, and advisors. The zonal council provides recommendations on a variety of problems to the Central Government and each State Government. Students can read all the details related to UPSC by visiting the official website of StudyIQ UPSC Online Coaching.


 Indian Secularism: Constitutional Provis...
Indian Secularism: Constitutional Provis...
 India Mediation Campaign, Objectives, Pr...
India Mediation Campaign, Objectives, Pr...
 Emergency Provisions in Indian Constitut...
Emergency Provisions in Indian Constitut...





















