Table of Contents
Union Budget 2023-24
The Union Budget is a yearly statement of finance of the Indian Republic. It is presented every year in the month of February generally as Annual Finance Statement. Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget 2023-24 in Parliament on 1st Feb 2023. She emphasized that the Indian economy is on the right track, and despite a time of challenges, heading towards a bright future. Nirmala Sitharaman is the sixth minister in independent India to present five consecutive budgets and she also presented the paperless budget three consecutive times in a row. Ministers who also have presented five straight annual financial statements in past include Arun Jaitley, P Chidambaram, Yashwant Sinha, Manmohan Singh and Morarji Desai.
Read More: Economic Survey 2022-23
Union Budget 2023-24 Objective
As it is being the first budget in the ‘Amrut Kal’ or Amrit Kaal, the Union Budget 2023 hopes to Build on the Foundation of a Prosperous, Inclusive India in which fruits of development reach all sections, said the finance minister.
In the 75th year of Independence, the world recognised the Indian economy as a bright star, she says. India has shown growth in spite of a slowdown globally owing to Covid-19. India’s GDP growth is estimated at 7% in FY-23.
Union Budget 2023-24 Highlights
- Senior Citizen Savings Scheme: FM announces an increase in the maximum investment limit from Rs. 15 lahks to Rs. 30 lahks.
- The Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana budget is being increased by 66% to more than 79,000 cr.
- To serve 3.5 lakh indigenous students in 740 Eklavya Model residential schools, the Center will hire 38,800 teachers and other staff.
- The Green Hydrogen Mission will make it easier for the economy to change so that it imports fewer fossil fuels.
- ITR processing time decreased from 93 days to 16 days on average.
- The updated credit guarantee for the MSME plan will go into effect on April 1, 2023, with a corpus injection of 9,000 crores. To cut the cost of credit by 1%.
- According to Budget 2023, DigiLocker will now serve as a one-stop KYC maintenance solution for people, allowing you to make changes to one document that will be reflected in all of your documents linked to DigiLocker.
Read More: Union Budget 2023 for Railways
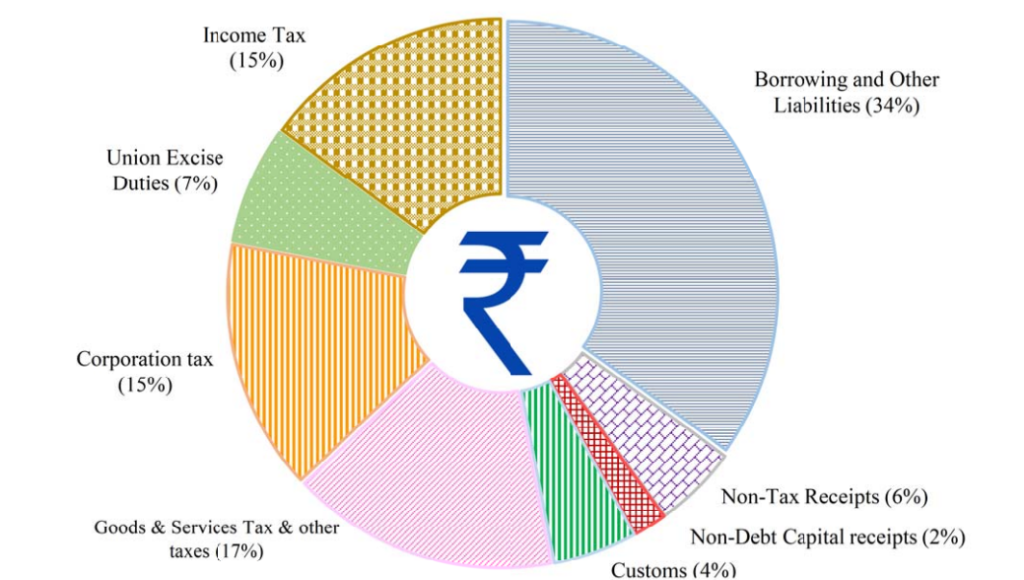
Rupee Come From (Revenue Receipt)
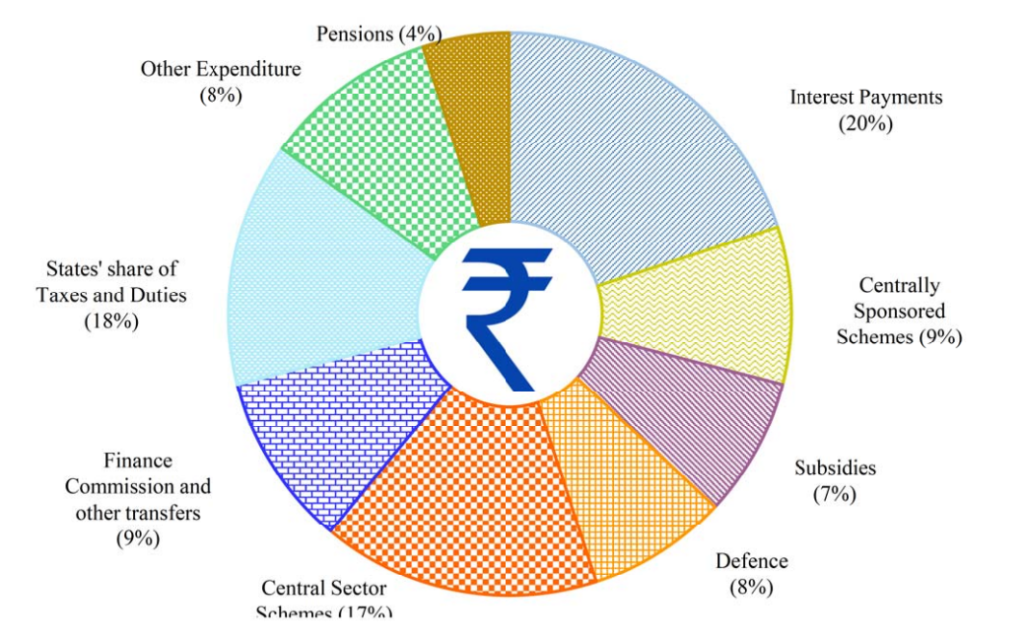
Rupees Goes To (Revenue Expenditure)
Union Budget 2023-24 Vision
For Amrit Kaal to become a knowledge-based, technology-driven economy with healthy public finances and a thriving financial sector, Jan Bhagidari’s Sabka Saath Sabka Prayas is crucial. The three main objectives of the plan for realising this goal are,

To service these focus areas in our journey to India@100, the following four opportunities can be transformative during Amrit Kaal are:
| Opportunities | Details |
| Economic Empowerment of Women | By organising rural women into 81 lakh Self Help Groups and enabling these groups to advance to the next stage of economic empowerment through the creation of sizable producer enterprises or collectives, each with several thousand members and professionally managed, the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana National Rural Livelihood Mission has achieved remarkable success. |
| PM VIshwakarma KAushal Samman (PM VIKAS) | The centuries-old tradition of art and craft in India represents the true spirit of Atmanirbhar Bharat. A package of assistance and the scheme enables to the improvement of the quality, reach and scale of the products integrating it with the MSME value chain. It will greatly benefit Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, OBCs, women and people belonging to the weaker sections. |
| Tourism | Due to its enormous tourism potential, the nation is incredibly alluring to both domestic and international visitors. Tourism promotion will be carried out in mission mode, with the active involvement of the states, the fusion of government initiatives, and public-private partnerships. |
| Green Growth | India is implementing many programmes for green fuel, green energy, green farming etc. which will help reduce the carbon intensity of the economy and provides for largescale green job opportunities. |
Union Budget 2023-24 India’s Accomplishments
India’s rising global profile is because of several accomplishments, such as Aadhaar, Cowin and UPI, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman says in her budget speech.
- Finance Minister claims that throughout the pandemic, the Narendra Modi administration made sure that nobody went to bed hungry.
- The centre will be responsible for paying the full Rs 2 lakh crore cost of the PM Gareeb Kalyan Anna Yojana.
- In relation to numerous sustainable development objectives, the administration has achieved tremendous progress.
- The fact that the membership of EPFO has doubled indicates how much more formalised the economy has become.
Union Budget 2023-24 Seven Priorities
There are seven priorities of Union Budget 2023-24, of which the Finance Minister talked about in her budget speech are:

The union government also aims to empower women by way of self-help groups (SHGs) focused on raw material supply, branding, and marketing of products, as stated by the finance minister. The seven priorities of Union Budget 2023-24 are discussed as:
Inclusive Development
Farmers, women, youth, OBCs, Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, divyangjan and economically disadvantaged groups have all benefited from inclusive development thanks to the government’s Sabka Saath Sabka Vikas concept, which also prioritises the underprivileged (vanchiton ko variyata). The North-East, Ladakh, and Jammu & Kashmir have also received consistent attention. This Budget furthers those initiatives.
| Priority | Development |
| Agriculture and Cooperatives | Building Digital Infrastructure
Through pertinent information services for crop planning and health, improved access to farm inputs, credit, and insurance, assistance for crop estimation, market intelligence, as well as support for the expansion of the agri-tech industry and startups, it will make it possible to implement inclusive, farmer-centric solutions. Agriculture Accelerator Fund It has been established to support young rural entrepreneurs who are starting agribusinesses with the goal of providing creative and economical solutions to problems faced by farmers. Modern technologies will also be introduced, changing farming practices and boosting production and profitability. Enhancing the Productivity of Cotton Crop The government will use Public-Private Partnerships to implement a cluster-based and value-chain approach to increase the productivity of extra-long staple cotton (PPP). This will entail partnerships between farmers, the government, and businesses for the provision of inputs, extension services, and market connections. Atmanirbhar Horticulture Clean Plant Programme An investment of Rs 2,200 crore would be made to increase the supply of high-value horticulture crops with disease-free, high-quality planting material. Global Hub for Millets: ‘Shree Anna’ India is the world’s greatest producer and second-largest exporter of “Shree Anna” due to the production of many kinds of this grain, including jowar, ragi, bajra, kuttu, ramdana, kangni, kutki, kodo, cheena, and sama. To make India a hub for “Shree Anna,” the Indian Institute of Millet Research in Hyderabad will be supported as the Center of Excellence for Sharing Best Practices, Research, and Technologies at the International Level. Agriculture Credit The goal for agricultural finance would rise to Rs 20 lakh crore, with an emphasis on dairy, fisheries, and animal husbandry. With a projected investment of Rs 6,000 crore, the government would introduce a new sub-scheme of the PM Matsya Sampada Yojana in order to enhance the operations of fish vendors, fishermen, and micro- and small businesses, increase the efficiency of the value chain and broaden the market. Cooperation A new Ministry of Cooperation was formed with a mandate to realize the vision of ‘Sahakar Se Samriddhi’ for promoting a cooperative-based economic development model. As a step toward this vision the government has already initiated the computerization of 10 of 63,000 Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) with an investment of Rs 2,516 crore The government will put into action a plan to establish a sizable decentralised storage capacity, which will assist farmers in storing their produce and obtaining profitable rates through timely sales. In the upcoming five years, the government would also support the establishment of numerous multipurpose cooperative societies, primary fisheries cooperative societies, and dairy cooperative societies in unorganised panchayats and villages. |
| Health | Affordable Health for All
|
| Education and Skill Development | Assessable Education and Skill development
|
Reaching the Last Mile
It focuses that ‘’No one should be left behind” by focusing on the socio-economic conditions of the particularly vulnerable tribal groups, drought-prone regions, housing, education, food supply and digitation of Ancient Inscriptions.
| Priority | Details |
| Aspirational Districts and Blocks Programme | The Aspirational Blocks Programme, which the government recently launched, covers 500 blocks and aims to saturate them with essential public services in a variety of areas, including health, nutrition, education, agriculture, water resources, financial inclusion, skill development, and basic infrastructure. |
| Pradhan Mantri PVTG Development Mission | The Pradhan Mantri PVTG Development Mission will be implemented to ameliorate the socioeconomic circumstances of the especially vulnerable tribal groups (PVTGs). This will offer PVTG families and habitations with basic necessities like safe housing, access to clean water and sanitation, improved health and nutrition, road and telecom connectivity, and opportunities for sustainable livelihoods.
To serve 3.5 lakh tribal students in 740 Eklavya Model Residential Schools, the Centre would hire 38,800 teachers and support personnel. |
| Water for Drought Prone Region | Drought-prone central region of Karnataka, central assistance of Rs 5,300 crore will be given to Upper Bhadra Project to provide sustainable micro irrigation and filling up of surface tanks for drinking water. |
| PM Awas Yojana | The outlay for PM Awas Yojana is being enhanced by 66 per cent to over Rs 79,000 crore.
One lakh old inscriptions will be digitally preserved as part of the “Bharat Shared Repository of Inscriptions,” which will be housed in a museum of digital epigraphy. |
Infrastructure & Investment
Infrastructure and productive capacity investments have a significant multiplier effect on growth and employment, and as a result, the capital investment outlay is being sharply boosted for the third year in a row by 33% to Rs 10 lakh crore, or 3.3% of GDP. The Center has budgeted Rs 13.7 lakh crore for “Effective Capital Expenditure,” or 4.5 per cent of GDP.
| Priority | Details |
| Support to State Governments for Capital Investment | To encourage infrastructure investment and to provide incentives for complementary policy initiatives, the government has decided to extend the 50-year interest-free loan to state governments for one more year with a significantly increased expenditure of Rs 1.3 lakh crore.
Public agencies will use the Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (UIDF), which will be administered by the National Housing Bank, to build urban infrastructure in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities. This fund will be established by the use of a priority sector loan deficit. |
| Railways | A capital outlay of Rs 2.40 lakh crore has been provided for the Railways, which is the highest ever outlay and about 9 times the outlay made in 2013- 14. |
Unleashing the Potential
For improving the ease of doing business, more than 39,000 compliances have been reduced and more than 3,400 legal provisions are being decriminalized. Jan Vishwas Bill to amend 42 Central Acts, Government has introduced for furthering the trust-based governance.
| Priority | Details |
| Centres of Excellence for Artificial Intelligence | Three centres of excellence for artificial intelligence will be established in prestigious educational institutions under the motto “Make AI in India and Make AI work for India.” |
| National Data Governance Policy | An Entity DigiLocker will be created for MSMEs, major businesses, and charitable trusts to use in order to securely store and share documents with various authorities, regulators, banks, and other business organisations as necessary.
In order to realise a new variety of options, business models, and employment potential, engineering colleges will construct approximately 100 labs for developing applications employing 5G services. |
Green Growth
An idea for “LiFE,” or “Living for the Environment,” to spur the development of a sustainable way of life. India is working toward the “panchamrit” and net-zero carbon emissions by 2070 in order to pave the way for a green industrial and economic revolution.
With an investment of Rs 19,700 crores, the recently launched National Green Hydrogen Mission will help the economy shift to low carbon intensity, lessen reliance on fossil fuel imports, and position India to assume technological and market leadership in the emerging sector.
| Priority | Details |
| GOBARdhan scheme | 500 new “waste to wealth” facilities will be built as part of the GOBARdhan (Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan) programme to advance the circular economy. With a total expenditure of Rs 10,000 crore, this consists of 200 compressed biogas (CBG) facilities, 75 of which are located in urban areas, and 300 community- or cluster-based plants. |
| Bhartiya Prakritik Kheti Bio-Input Resource Centres | The Center will assist one crore farmers in switching to ecological farming during the next three years. 10,000 Bio-Input Resource Centers will be established for this, resulting in the development of a distributed national micro-fertilizer and pesticide manufacturing network. |
Youth Power
The government has formulated the National Education Policy, focused on skills, adopted economic policies that facilitate job creation at scale, and supported business opportunities for the ‘Amrit Peedhi’.
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 is being launched for skilling lakhs of youth within the next three years. On-job training, industrial partnership, and alignment of courses with the needs of the industry will be emphasized. The scheme will also cover new-age courses for Industry 4.0 as coding, AI, robotics, mechatronics, IOT, 3D printing, drones, and soft skills.
| Priority | Details |
| National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme | A pan-India National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme will use Direct Benefit Transfer to give stipend support to 47 lakh youth over the course of three years. |
| Unity Mall | States will be encouraged to set up a Unity Mall in their state capital or most prominent tourism centre or financial capital for the promotion and sailing of their ODOPs (one district, one product), GI products and other handicraft products, and to provide space for such products of all the States. |
Financial Sector
By injecting Rs 9,000 crore into the corpus, the loan guarantee scheme for MSMEs will be revised and announced, and it will go into operation on April 1, 2023. An additional Rs 2 lakh crore in collateral-free guaranteed loans will be made possible as a result. Additionally, the cost of borrowing will be decreased by 1%.
With the creation of the National Financial Information Registry, financial and associated data will have a central location. As a result, financial stability, effective credit flow, and financial inclusion will be promoted.
Senior Citizens
As per Union Budget 2023 the Senior Citizen Savings Scheme’s maximum deposit limit will increase from Rs 15 lakh to Rs 30 lakh, according to the Finance Minister. Additionally, the monthly income account scheme’s maximum deposit limit would increase from Rs 4.5 lakh to Rs 9 lakh for single accounts and from Rs 9 lakh to Rs 15 lakh for joint accounts.
Union Budget 2023-24 Key Proposals
During the Union Budget 2023 speech, the honorable finance minister proposed some key initiatives:
- Set up a PM Primitive Vulnerable Tribal Groups Mission for improving the socio-economic conditions of vulnerable tribal groups.
- Set up a national digital library for children and adolescents to make up for their loss of learning during the pandemic of Covid-19.
- The Government will launch the Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme for improving the availability of disease-free quality planting material for high-value horticultural crops at an outlay of Rs 2,200 crore.
- The government had planned to set up an agriculture accelerator fund to encourage startups in rural areas.
- The government will be setting up 30 Skill India international centres in multiple states.
- The government will be setting up a National Financial Information Registry to serve as a central repository of financial and ancillary information.
- PM PRANAM Yojna is to be launched for incentivising the States and Union Territories to promote alternative fertilisers and balanced use of chemical fertilisers.
- The government will be launching Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0. The objective is to skill the youth for international opportunities, 30 Skill India International Centres will be set up across different States.
Union Budget 2023-24 Key Targets
There are some major Key Targets mentioned in the Union Budget 2023 such as:
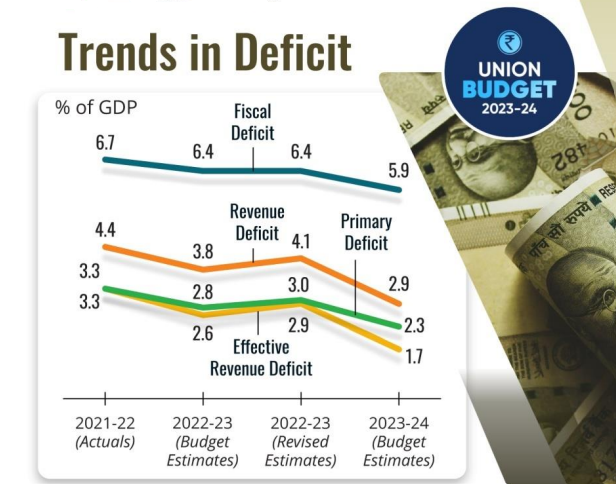
- The gross borrowing target for Financial Year-24 is ₹15.43 lakh crore.
- The target for Fiscal deficit for the Financial Year-24 is 5.9%.
- Fiscal deficit for Financial Year-23 estimated at 6.4% of GDP.
- The fiscal deficit glide path for Financial Year-26 is 4.5%.
- Duties will be increased on silver doors, and bars at par with gold.
- Big push to ‘Make in India’. LI battery, mobile, tv, and chimney manufacturing get custom rebates.
Union Budget Estimates 2023-24
- Total Receipt (other than borrowing) is Rs. 27.2 lakh Cr
- Total Expenditure Rs 45 Lakh Cr
- Net Tax Receipt Rs 23. 3 Lakh Cr
Union Budget 2023-24 Tax Slabs
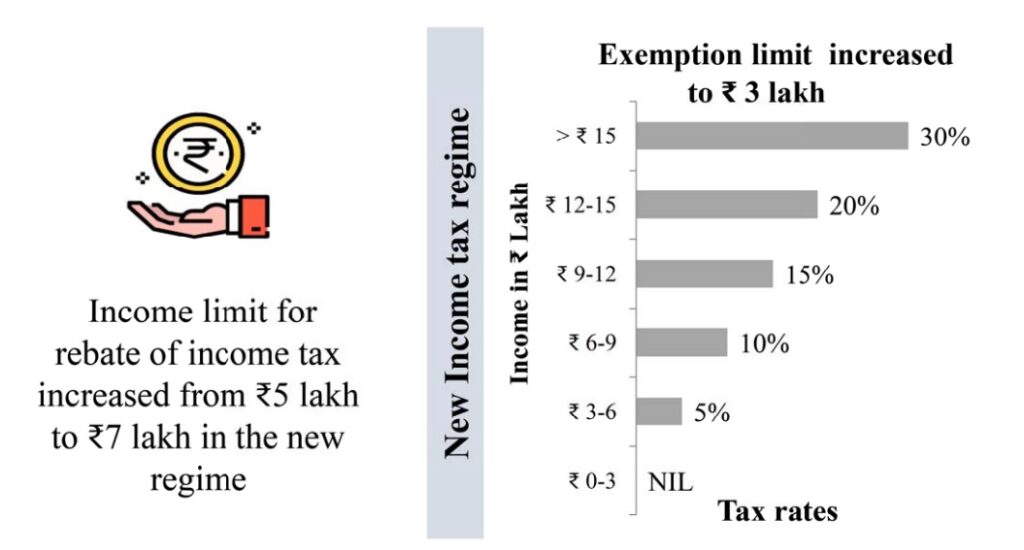
In the Union Budget 2023, union government has increased the income rebate limit to Rs 7 lakh from Rs 5 lakh under the new tax regime. Hence, persons in the new tax regime, having an income of Rs. 7 lahks do not have to pay any tax. The new tax regime will now be a default tax regime, but citizens can still avail of benefits under the old tax regime on an opt-out basis,
Further Simplification of Taxation
- To reduce the surcharge rate for those earning more than Rs 50 lakh from 37% to 25% in the new tax regime.
- Extending benefits of the standard deduction to the new tax regime for salaried class and pensioners.
- Increased tax exemption limit to Rs 25 lakhs on leave encashment on retirement for non-government salaried employees.
- The new tax regime will now be a default tax regime, but citizens can still avail of benefits under the old tax regime on an opt-out basis.
Union Budget 2023-24 Indirect Tax Simplification
Union Budget 2023 with an aim to promote exports, boost domestic manufacturing, enhance domestic value addition and encourage green energy and mobility simplification of indirect tax has been addressed. A simplified tax structure with fewer tax rates helps in reducing compliance burden and improving tax administration which will help to deliver.
Union Budget Constitutional Provision
Our Constitution of India makes no mention of the word “budget.” According to Article 112 of the constitution, the annual financial statement is referred to as the union budget. It is a statement of the government’s estimated receipts and outlays for a given fiscal year. includes the following in the budget:
- It provides the estimations of revenue and capital receipts,
- Provides the Ways and means to raise revenue,
- Estimation of expenditure,
- Details of the actual receipts and expenditure of the closing financial year and the reasons for any deficit or surplus in that year, and
- The economic and financial policy of the upcoming year, i.e., taxation proposals, prospects of revenue, spending programme and introduction of new schemes/projects.
Union Budget Objective and Significance
- Allocating resources in such a way that benefits society as a whole and is in the best interests of the general welfare.
- It uplifts and motivates the underprivileged sections in society by lowering poverty rates and generating employment.
- Establishes policies for ensuring that all the people have access to necessities including food, shelter, healthcare, and education.
- It ensures that money is distributed fairly through taxes and other financial aid.
- To control inflation, deflation, and economic swings will guarantee the nation’s economic stability and growth.
In 2017, the year-old tradition of presenting the Railway and General budgets separately (started in 1924) was broken when the railway budget was merged with the Union Budget and presented together, it was merged on the recommendations of the Vibek Debroy Committee.


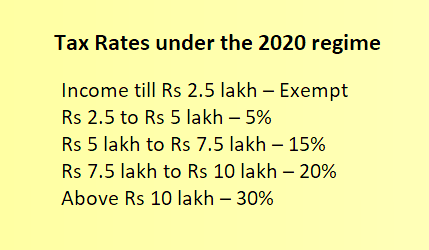
 Goods and Services Tax (GST), Objectives...
Goods and Services Tax (GST), Objectives...
 World Oceans Day 2025, History, Theme, S...
World Oceans Day 2025, History, Theme, S...
 World Environment Day 2025, Theme, Histo...
World Environment Day 2025, Theme, Histo...





















