Table of Contents
Context: Lokpal gave a clean chit to Madhabi Puri Buch, former SEBI Chairperson, by disposing of all complaints filed in the Hindenburg-Adani case, marking a significant judgment.
About Lokpal
- Lokpal is a statutory body established under the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act 2013 to inquire into and investigate allegations of corruption against public functionaries, including the Prime Minister, Ministers, and Members of Parliament.
- Lokpal (Amendment) Act 2016: Allows the leader of the largest opposition party in the Lok Sabha, in the absence of a recognised Leader of Opposition, to be a member of the selection committee.
- Jurisdiction: Prime Minister, Ministers, Members of Parliament and groups A, B, C, and D of government employees.
- First Lokpal Chairperson: Justice Pinaki Chandra Ghose (appointed in 2019)
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Independent body not under the control of any ministry.
Composition
- Chairperson (Retd./Serving Chief Justice of India/ Judge of the Supreme Court or an eminent person who fulfils the eligibility specified in the act)
- Members: A Maximum of eight Members, out of whom 50% are Judicial Members.
- Reservation: At least 50% of Lokpal members should belong to SC/ ST, OBC, Minorities and Women.
- Tenure: They hold office for a term of 5 years from the date on which they enter upon the office or until they attain the age of 70 years, whichever is earlier.
Appointment Process of Lokpal
The President appoints the Chairperson and the Members on the recommendations of a Selection Committee consisting of:
- Chairperson: Prime Minister as Chairperson
- Members: Speaker of Lok Sabha, Leader of Opposition Lok Sabha, Chief Justice of India, and one eminent jurist to be nominated by the President on the recommendation of the Chairperson and the members of the Selection Committee.
Jurisdiction (Under Section-14 of the Lokpal Act)
Prime Minister, Ministers, Members of Parliament and groups A, B, C, and D of government employees. PM is included with some exceptions (national security, international relations, etc.).
Examination of Applicability to Judges and CJIs
- Judges, including those of the Supreme Court, are “public servants” as per Section 2(c) of the Prevention of Corruption (PC) Act, 1988.
- However, the Supreme Court is not a “body established by an Act of Parliament” but by Article 124 of the Constitution of India.
Interpretation of Section 14(1)(f)
- Section 14(1)(f) applies to entities established by an Act of Parliament or controlled/financed by the central government.
- Lokpal clarified that:
- The Supreme Court does not qualify as such a body.
- Judges and the CJI are not controlled or financed by the central government.
| Facts |
|
Powers and Functions
- Can conduct preliminary inquiry, investigation, and prosecution.
- Refers cases to CBI or other agencies.
- Has the powers of a civil court during inquiries.
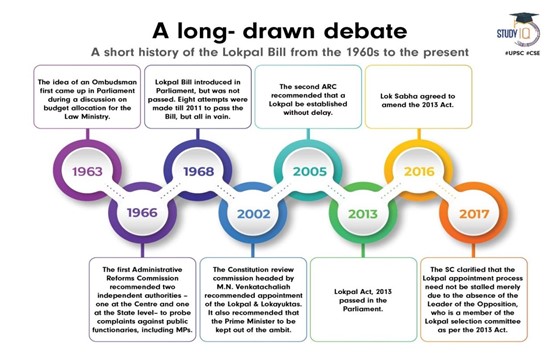
Background About Lokpal: History
Laxmi Mall Singhvi, a member of parliament, coined the term “Lokpal” for the first time in 1963 during a discussion on grievance redressal procedures. A report produced by the Administrative Reforms Commissions under Morarji Desai suggested the establishment of the Lokayukta and Lokpal special authorities to address public complaints.
The Maharashtra Lokayukta and Upa-Lokayuktas Act passed in 1971, made Maharashtra the first state to implement the Lokayukta system. The states of Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, and Tripura do not currently have any Lokayuktas.
In 1968, the Lokpal Bill was first brought before the Lok Sabha. The draught that was used to create the 2013 edition was created in 2010. The Prevention of Corruption Act of 1988 is being put into practice by this bill. The bill was passed against the backdrop of the nation-shaking, massive anti-corruption demonstrations led by Anna Hazare.
Current Lokpal of India
Shri Justice Ajay Manikrao Khanwilkar is the Present Lokpal of India, The important information is as follows:
- Birth: Born on July 30, 1957.
- Education: Completed B.Com from Mulund College of Commerce and L.L.B. from K.C. Law College in Mumbai.
- Advocate: Enrolled as an Advocate on February 10, 1982.
- Bombay High Court: Became Additional Judge on March 29, 2000, and was confirmed as a permanent Judge on April 8, 2002.
- Chief Justice of Himachal Pradesh High Court from April 4, 2013.
- Chief Justice of Madhya Pradesh High Court from November 24, 2013.
- Elevated to the Supreme Court of India on May 13, 2016, and served until July 29, 2022.
- National Sports Awards: Nominated as Chairperson of the Selection Committee for the National Sports Awards in 2022 and 2023.
- News Broadcasters Federation: Served as Chairperson of the self-regulatory body, NBF-Professional News Broadcasters Standards Authority.
- Mahanadi Water Disputes Tribunal: Nominated as Chairman while serving as a Supreme Court Judge and continued as full-time Chairman until March 8, 2024.
- Lokpal of India: Appointed as Chairperson of Lokpal on March 10, 2024 Nearly two years after the position became vacant following the completion of Justice Pinaki Chandra Ghose’s term in May 2022.
Lokpal Act 2013
The Act establishes an anti-corruption ombudsman called Lokpal at the national level and Lokayukta at the state level.
- Lokpal will have a chairperson and up to eight members.
- It applies to all public servants, including the Prime Minister, but not to the armed forces.
- The Act allows for the confiscation of property gained through corruption, even if legal action is still ongoing.
- States must set up Lokayukta within one year of the Act’s start.
- Public servants who report corruption are protected.
Lokpal Composition
Composition of Lokpal: The Lokpal panel includes:
- A chairperson.
- At least 8 members.
- 4 of these members must be judges.
Understanding Regulations: For detailed information on regulations and eligibility criteria for the Lokpal and Lokayukta selection committees, review the relevant topics provided.
Eligibility Criteria for Lokpal Members
The Lok Pal chairperson ought to have held a position as India’s chief justice, a Supreme Court judge, or another illustrious figure with knowledge and experience in the fields of anti-corruption strategy, vigilance, public administration, law, and management.
The Lokpal judicial member ought to have been a Chief Justice of the High Court or a judge on the Supreme Court. Any distinguished individual with 25 years of experience in public administration, vigilance, and anti-corruption policies is eligible to serve as a member of the Lokpal. The scheduled castes, scheduled tribes, and OBC, as well as women and minority classes, shall make up half of the Lokpal membership.
Selection Committee
A selection committee made up of the Prime Minister, the Speaker of the Lok Sabha, the head of the opposition in the Lok Sabha, and the CJI appoints all members of the Lokpal.
Lokpal Complaint Rules 2020
These rules, established under the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, outline how to file complaints.
- Complainants must provide a valid ID. Foreign nationals can use a copy of their passport.
- Complaints can be submitted online, by mail, or in person. If filed electronically, a hard copy must be sent within 15 days
- No complaints can be made against public servants under military laws (Army, Navy, Air Force, Coast Guard).
- Complaints can be in English or any language from the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution.
- Complainants must include details about the accused, allegations, evidence, and an affidavit. Organisations must provide registration and authorisation certificates.
- The Lokpal will review complaints at the admission stage and may request more information if needed.
- The identity of complainants and accused is protected until the inquiry is complete unless the complainant discloses their identity elsewhere.
- Complaints that are unclear, trivial, lack allegations, are over seven years old or are already pending elsewhere will be disposed of within 30 days.
Lokpal Limitations
The Lokpal was a tool the Indian government employed to fight corruption. But some flaws and gaps need to be filled. The Lokpal selection procedure is biased since there are no standards for determining who qualifies as an “eminent jurist” or “a person of integrity.” Lokpal’s acts cannot be challenged according to established processes.
According to the Lokpal and Lokayukta Act, corruption complaints cannot be submitted until seven years have passed after the accused offence was committed. Political party representatives make up the Lokpal appointment committee, and they attempt to influence Lokpal’s decisions.
- Cannot probe allegations against the PM in matters of:
- International relations
- External/internal security
- Public order
- Atomic energy and space (unless a full bench agrees and approves)
The Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act 2013 was passed by Parliament five years ago, but no Lokpal has been appointed since, which suggests a lack of political will. One of the gravest issues with the Lokpal is that the judiciary is not included in its ambit. The decisions made by Lokpal lack a legal foundation, and there are no effective means of challenging them.


 Indian Secularism: Constitutional Provis...
Indian Secularism: Constitutional Provis...
 India Mediation Campaign, Objectives, Pr...
India Mediation Campaign, Objectives, Pr...
 Emergency Provisions in Indian Constitut...
Emergency Provisions in Indian Constitut...





















