Table of Contents
Context: The contemporary world is undergoing a phase of unprecedented geopolitical and economic disruption, driven by volatile leadership, shifting power structures, and resurgent regional conflicts.
What are the Current Global Crises?
United States (U.S.)
President Donald Trump’s transactional approach to diplomacy and protectionist economic policies, notably the tariff war, exacerbated global instability.
- The U.S., once a beacon of democratic stability, now grapples with deep internal divisions and declining global influence, marked by hostile immigration policies and attacks on educational institutions.
- Eg., Restrictions on foreign students (who contribute $40+ billion/year and support 400,000+ jobs) harm U.S. soft power and economy.
Europe
Europe is weakened by its Ukraine conflict and doubts over NATO’s future.
West Asia
- Israel’s aggressive stance in Gaza and Syria, aided by Western inaction, signals an attempt to reshape regional geography.
- The possible Israeli strike on Iran and turmoil in Türkiye further intensify tensions.
Africa
Old conflicts, like Ethiopia-Eritrea, have resurfaced.
- The resurgence of Islamic State affiliates across Africa and Asia (such as in Mozambique, Congo, North Africa & Afghanistan) heightens security concerns.
Asia
- Afghanistan and Pakistan: Afghanistan and Pakistan are facing severe internal chaos and a surge in terrorism.
- Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Nepal: Internal instability grips Bangladesh (governance issues), Myanmar (post-coup conflict), and Nepal (political uncertainty), weakening regional coherence.
- China’s Assertiveness: Amid economic slowdown, China is intensifying pressure on Taiwan, countering U.S. tariffs, and asserting influence through economic and peace offensives in Southeast Asia.
- Geopolitical Tilt in Asia: With the U.S. retreating, many Asian nations are tilting towards China, which is expanding its naval footprint into the Indian Ocean and South Pacific, beyond its “nine-dash line.”
- India-China Tensions: Despite recent border accords, strategic India-China rivalry persists, requiring India to counter Af-Pak-based terror threats and prepare for the containment of China in the Indo-Pacific.
Conclusion
- The world is entering a new disorder driven by:
- Disruptive leadership.
- Disintegrating multilateral institutions.
- Widening economic inequality.
- Technological and military shifts.
- The “old world order“ is crumbling, with no stable replacement yet in sight.
- Regions across the world, from the U.S. to Asia and West Asia, are undergoing deep fragmentation, requiring nations like India to adopt strategic agility, regional vigilance, and internal resilience.
|
Comparative Analysis of Global Regions |
||
| Region/Country | Pre-COVID Scenario | Post-COVID Scenario |
| United States | Stable GDP growth (~2.3% in 2019)
Trade dominance Global leadership in finance and military |
Inflation spikes (peaked at 9.1% in 2022)
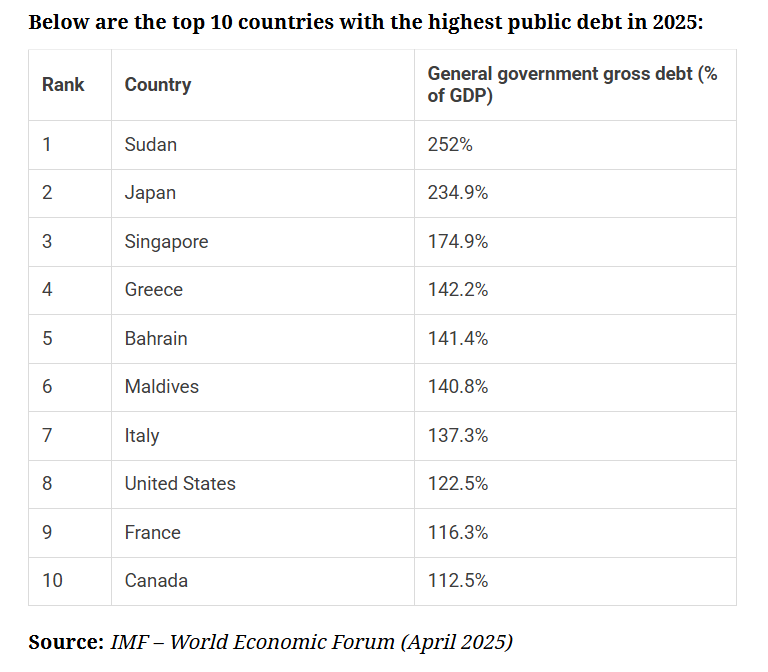
High public debt (~123% of GDP in 2025) Protectionist trade under Trump, “America First” policy |
| European Union | ➔ Economic integration, single market
➔ Brexit pending, but still cohesive ➔ Moderate growth (1.6% in 2019) |
➔ Brexit completed (2020)
➔ Energy crisis due to the Russia-Ukraine war ➔ Sluggish growth, 0.8% in 2023 |
| Middle East & North Africa (MENA) | ➔ Oil-driven economies
➔ High youth unemployment ➔ Ongoing regional rivalries |
➔ Oil prices are volatile
➔ Conflicts escalated (e.g., Gaza, Syria) ➔ Push for economic diversification (Saudi Vision 2030) |
| Africa | ➔ GDP growth of 3.4% (2019)
➔ Foreign investment in infrastructure ➔ Debt moderately high (~50% of GDP) |
➔ Food security issues post-Ukraine war
➔ Debt distress in 22+ nations |
| China | ➔ Manufacturing hub
➔ 6%+ annual GDP growth ➔ Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) expanding |
➔ Growth slowed to 5.2% in 2023
➔ Ageing population crisis ➔ Global pushback on BRI, tech sanctions |
| Latin America | ➔ Commodity-based growth
➔ Democratic progress ➔ Debt levels high but stable (~60% of GDP) |
➔ Growth slowed to ~1.9% in 2023
➔ Political turmoil in Peru, Argentina, Brazil ➔ High inflation, currency instability |


 German Chancellor Visit to India in 2026...
German Chancellor Visit to India in 2026...
 Iran Nuclear Crisis and India’s Role f...
Iran Nuclear Crisis and India’s Role f...
 H1B Visa Program, Beneficiaries, Eligibi...
H1B Visa Program, Beneficiaries, Eligibi...




















