Table of Contents
Context: The Russia-Ukraine conflict has escalated significantly, marked by intensified military actions and renewed diplomatic efforts.
Russia-Ukraine War Latest Updates
Ukraine Hits Russian Bridge with Underwater Explosives
On 3 June 2025, Ukraine’s Security Service (SBU) carried out a major underwater sabotage on the Kerch Bridge, a strategic infrastructure connection between mainland Russia and the annexed Crimean peninsula. The action was based on planting and detonating about 1,100 kilograms (2,420 pounds) of explosives under the support pillars of the bridge, inflicting heavy damage on its underwater pillars.
The Kerch Bridge, which was opened by Russian President Vladimir Putin in 2018, is 19 kilometres long and runs across the Kerch Strait. It is a critical supply line for Russian forces in Ukraine. This is the third attack on the bridge by Ukrainian forces, preceded by attacks in October 2022 and July 2023.
Ukrainian Drones Strike Russian Airbase
On June 1, Ukraine conducted “Operation Spider’s Web,” a simultaneous drone attack of five Russian airbases in different regions, such as Siberia and Murmansk. Employing 117 FPV drones hidden inside refurbished trucks, the operation reportedly destroyed or damaged more than 40 Russian military aircraft, particularly strategic bombers such as the Tu-95 and Tu-22 types. This historic push deep into Russian airspace caused an estimated $7 billion in damages and briefly limited Russia’s long-range strike capabilities.
In response, Russia escalated its attack, launching drone and missile strikes throughout Ukraine. Aerial bombings in the area around Zaporizhzhia killed five civilians, with drone attacks in the Sumy district wounding at least six people, including children.
Diplomatic Efforts and Peace Talks
Istanbul Peace Negotiations
Despite the growing hostilities, Russian and Ukrainian envoys met in Istanbul on June 2 for their second round of direct peace negotiations since 2022. Ukraine introduced a blueprint calling for an initial 30-day ceasefire, exchange of prisoners, and a summit between Presidents Zelenskyy and Putin. Much remains in contention, notably territorial concessions and reparations, raising doubts over the possibility of an immediate solution.
International Reactions
US Senators Lindsey Graham and Richard Blumenthal were concerned about Russia’s motive, speculating that President Putin is dragging out negotiations in preparation for additional military attacks. They underscored the importance of imposing tight sanctions on countries that back Russia’s war economy.
Origin of the Russia-Ukraine War
- February 24, 2022: Russian President Vladimir Putin launched the invasion of Ukraine, expecting a quick victory.
- Western countries, including the U.S., initially anticipated Ukraine’s fall, evacuating their embassies from Kyiv.
- However, Ukraine’s resistance, backed by S.-supplied weapons, prevented an early Russian victory.
- The Biden administration adopted a two-pronged strategy:
- Sanctions on Russia to weaken its war economy.
- Massive military aid to Ukraine to counter the Russian invasion.
Russian Setbacks
- September 2022: Russia withdrew from Kharkiv Oblast in the northeast.
- November 2022: Russian forces pulled back from Kherson city and parts of Mykolaiv in the south.
Russia’s Counterstrategy
- Annexed four Ukrainian oblasts (Donetsk, Luhansk, Zaporizhzhia, Kherson).
- Partial mobilisation of troops to prepare for a prolonged war.
- Economic pivot to Asia, leveraging markets in China and India to bypass Western sanctions.
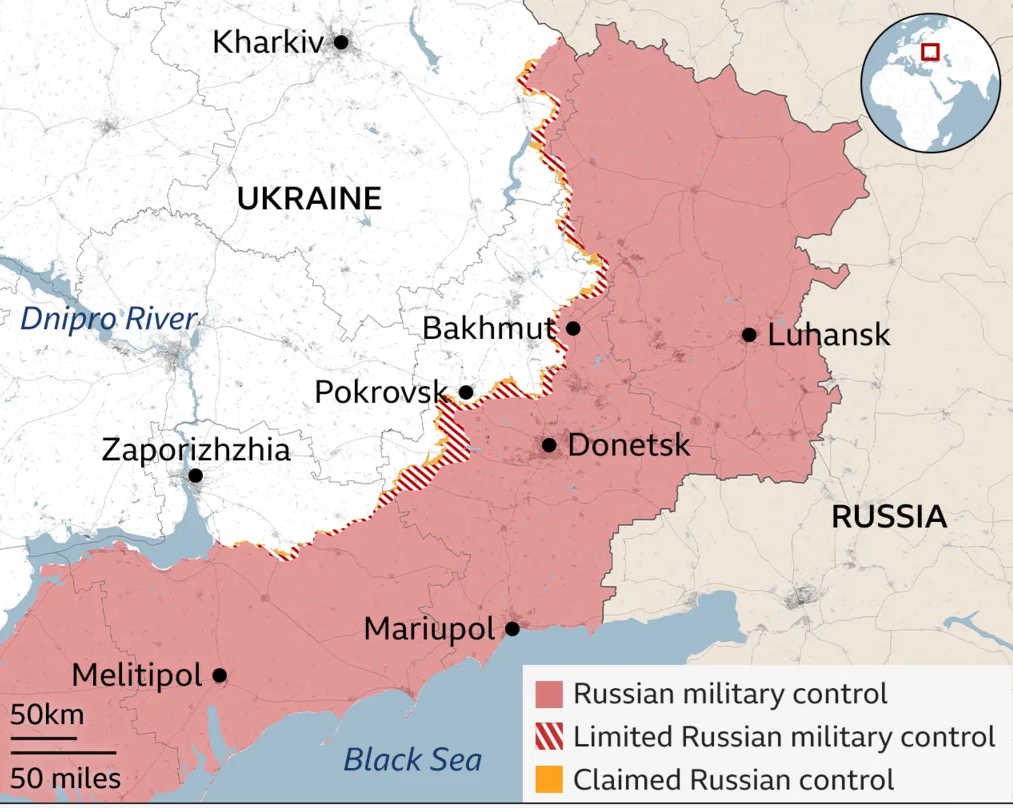
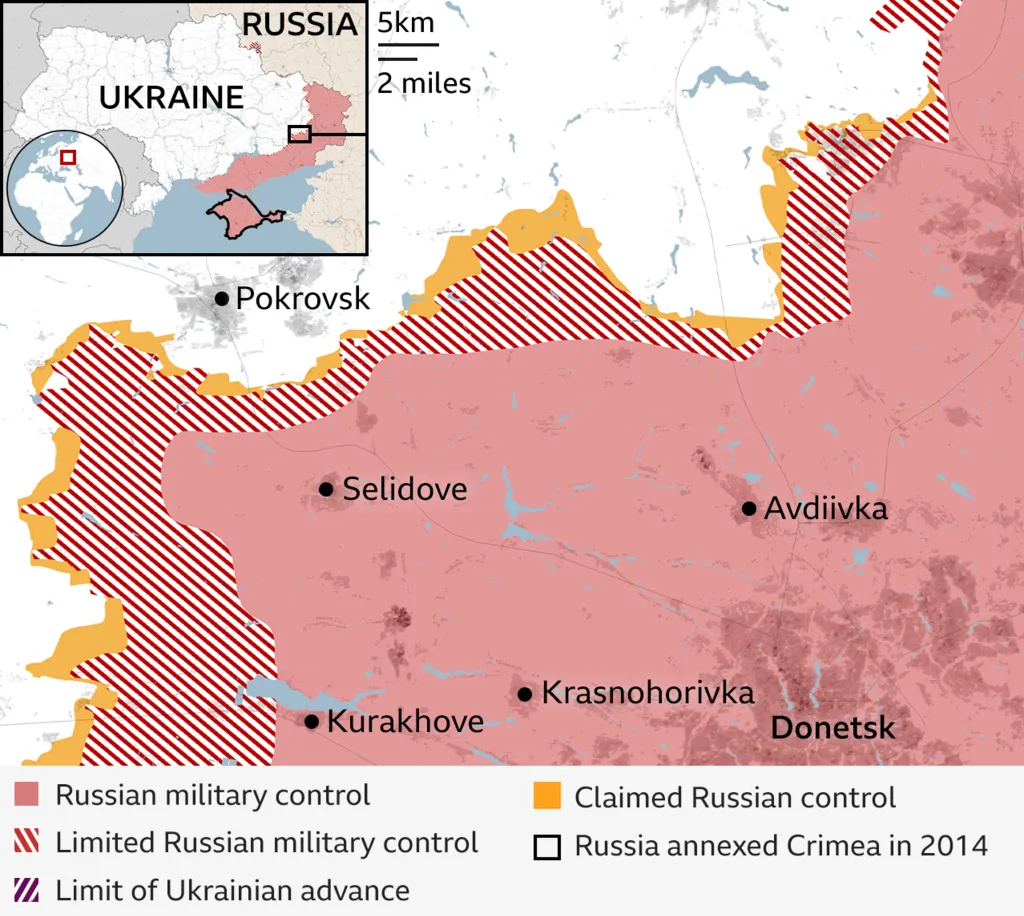
Development of Russia-Ukraine War
- 2023: Russia began regaining lost ground, securing key locations:
- Soledar (January 2023)
- Bakhmut (May 2023)
- 2024: Russian forces captured:
- Avdiivka (February 2024)
- Krasnohorivka (September 2024)
- Vuhledar (October 2024)
- Ukrainian counteroffensive (June 2023): Launched with advanced Western weapons but failed against Russia’s strong defences.
- August 2024: Ukraine launched a surprise attack in Russia’s Kursk region, capturing 1,000 sq. km to pressure Russian advances in the east.
- Russia’s counter-counteroffensive:
- Ignored the Kursk attack and focused on Ukraine’s eastern weaknesses.
- By 2024, Russia had captured 4,168 sq. km in both Ukraine and Russia’s Kursk region.
- January 2025: Russian troops seized:
- Velyka Novosilka
- Parts of Toretsk
- Attempted encirclement of Pokrovsk
- Ukraine’s strategy:
- Intensified drone and missile attacks deep inside Russia and in the Black Sea.
- However, remained on the backfoot militarily for over two years.
| Aspect | European Perspective | U.S. Perspective |
| Initial Response to the War | Supported Ukraine but was hesitant about escalation; economic concerns over energy dependence on Russia. | Adopted a two-pronged approach: sanctions on Russia and military aid to Ukraine. |
| Military Support | European countries provided military aid but lacked the capacity for long-term independent support. | Supplied advanced weapons, intelligence, and financial assistance. |
| Economic Costs & Challenges | Faced economic hardships due to the loss of Russian gas (Nord Stream pipeline sabotage), leading to a cost-of-living crisis and deindustrialisation. | The U.S. economy remained largely unaffected by the war, allowing it to sustain military aid. |
| NATO Membership for Ukraine | Initially hesitant in 2008 (France & Germany opposed it). Now, seeks security guarantees but lacks consensus on how to provide them. | Initially supported NATO membership for Ukraine but under Trump, abandoned it and ruled out security guarantees. |
| Security Concerns | Fears Russia’s expansionism but lacks a unified defence strategy without U.S. leadership in NATO. | Prioritises a strategic shift, seeing China as a bigger threat rather than Russia. |
| Policy Shift Under Trump | Caught off guard by the sudden U.S. reversal, now scrambling to reassess its role in the conflict. | Under Trump, shifted towards realignment with Russia, focusing on great power politics over Ukraine’s interests. |
| Long-Term Strategy | Wants continued deterrence against Russia but lacks independent military strength. | Aims to reconfigure global strategy by ending the war and preventing a China-Russia alliance. |
| Key Challenges | Economic downturn, rise of far-right movements, uncertainty over NATO’s future. | Managing relations with both Russia and China while ensuring a controlled exit from the war. |
Situation in Ukraine
Massive losses
- Lost over 20% of its territory.
- Tens of thousands of soldiers killed.
- Millions of Ukrainians displaced.
Economic Collapse
- Infrastructure and energy sector severely damaged by Russian bombings.
- Dependent on external military supplies (artillery, ammunition, weapons).
- Facing a manpower shortage on the battlefield.
Bleak Future
- S. withdrawal of support makes a Ukrainian victory nearly impossible.
- No NATO membership or security guarantees.
- Continuing the war risks more territorial losses.
- Stopping the war means accepting a deal shaped by Russia and the U.S.
Final Analysis
- Great powers use proxy wars for their strategic interests.
- They reset ties when those interests align.
- Ukraine is left with no good options, a stark reminder of how proxies suffer in global power struggles.
Russia-Ukraine War: Background
| Event | Date | Description |
| Beginning of the conflict | February 2014 | Conflict was initiated with Russia’s annexation of Crimea from Ukraine, followed by support for pro-Russian separatists in the Donbas region. |
| Expansion of conflict | April 2014 | Russians and local proxy forces seized territory in Ukraine’s Donbas region, escalating the conflict. |
| Full-scale invasion | February 24, 2022 | Russia launched a comprehensive invasion of Ukraine, intensifying hostilities and leading to widespread devastation. |
| Start of Donbas war | April 2014 | Armed Russian-backed separatists seized control of Ukrainian government buildings, declaring the Donetsk People’s Republic and Luhansk People’s Republic as independent entities. |
| Human casualties | 2014 – present | Over 14,000 casualties were reported, with the United Nations estimating 14,200-14,400 deaths in the ongoing conflict in eastern Ukraine. |
Russia-Ukraine War at a Glance Timeline
| Month | Year | Events |
| February | 2022 | Russia invades Ukraine; fierce fighting around Kyiv; EU opens doors to Ukrainian refugees; UN condemns aggression; West imposes sanctions. |
| March | 2022 | Shockwaves of invasion felt globally; grizzly evidence of war crimes in Bucha emerges; Russian advance stalls; crackdown on media and opposition in Russia. |
| April | 2022 | Russian missile strike kills civilians in Kramatorsk; new offensive in Donetsk and Luhansk regions; Ukrainian forces recapture Snake Island. |
| May | 2022 | Sweden and Finland bid to join NATO; Russia holds Victory Day Parade; Ukraine wins Eurovision; Azovstal steel mill resistance ends. |
| June | 2022 | 100 days of war; Western brands exit Russia; looming global food crisis; Ukrainian forces recapture Snake Island. |
| July | 2022 | Last city in Luhansk falls to Russia; inflation hits record highs in Eurozone; periodic shutdowns of Nord Stream gas pipelines begin. |
| August | 2022 | Amnesty report accuses Ukraine of civilian endangerment; explosions at airbase in Crimea; gas exports to Europe halt. |
| September | 2022 | Ukraine launches counter-offensive in Kharkiv; Putin announces partial mobilization; Russia annexes regions. |
| October | 2022 | Explosion damages Crimean bridge; Ukraine accused of corruption; global food crisis worsens; Ukraine recaptures Kherson. |
| November | 2022 | Ukrainian forces enter Kherson; blast near Ukrainian border kills two; NATO promises Ukrainian membership. |
| December | 2022 | Zelenskyy visits US; Biden promises Patriot systems; fears of renewed Russian offensive; Putin claims readiness for negotiation. |
| January | 2023 | Germany agrees to supply tanks to Ukraine; Ukraine withdraws from Soledar; Russia-Belarus joint drills begin. |
| February | 2023 | Corruption scandal hits Ukrainian Defence Ministry; historic summit between Kyiv and EU; rallies mark one year since invasion. |
| March | 2023 | Bitter fighting in Bakhmut; Ukraine receives first delivery of Western tanks; Russia wants to move nukes to Belarus. |
| April | 2023 | US intelligence leak reveals classified information; EU resolves dispute over Ukrainian grain; Russian bombardments intensify. |
| May | 2023 | Whispers of Ukrainian counteroffensive; EU warns of potential Ukrainian collapse; growing rift between Russian army and Wagner. |
| June | 2023 | Explosion at Nova Kakhovka dam; Ukraine’s counteroffensive begins; Wagner mercenaries rebel against Russian leadership. |
| July | 2023 | NATO summit disappoints Ukraine; accusations of landmine usage; US sends cluster bombs to Ukraine; China likely supplies Russia’s war effort. |
| August | 2023 | Russia claims full control of Avdiivka; Amnesty International publishes report on Ukraine’s Defence Ministry corruption. |
| September–November | 2023 | Fighting continues with high casualties on both sides; frontlines remain largely unchanged. |
| December | 2023 | Russia captures Bakhmut after prolonged battles, marking a symbolic victory. |
| March | 2024 | Russia regains momentum with a renewed offensive in the Kharkiv region, exploiting Ukrainian supply challenges. |
| April–July | 2024 | Intense fighting continues; Ukraine faces difficulties due to shortages in weapons and ammunition. |
| August–December | 2024 | Ukraine conducts targeted drone strikes on Russian military assets, including naval vessels and supply lines. |
| January | 2025 | A significant drone attack in Kyiv results in casualties and damage to infrastructure. |
| March | 2025 | Ukraine launches a cross-border incursion into Russia’s Belgorod Oblast, marking a bold escalation in the conflict. |
| May | 2025 | Ukraine executes “Operation Spider’s Web,” a large-scale drone assault on Russian airbases, reportedly damaging over 40 aircraft and causing substantial losses. |
| June | 2025 | Despite ongoing hostilities, peace talks are scheduled in Istanbul. Ukraine proposes a 30-day ceasefire and prisoner exchanges, while Russia demands Ukraine’s neutrality and cessation of NATO aspirations. |
Russia-Ukraine Military Conflict
The conflict has resulted in a devastating toll on both civilian populations and military personnel. Despite multiple ceasefires and diplomatic efforts to de-escalate tensions, sporadic fighting continues along the frontlines, exacerbating the humanitarian crisis and hindering prospects for peace.
The use of heavy weaponry, including artillery and missiles, has led to widespread destruction of infrastructure and civilian casualties. Both sides have been accused of human rights abuses and war crimes, including indiscriminate shelling of civilian areas and the targeting of critical infrastructure such as hospitals and schools.


 German Chancellor Visit to India in 2026...
German Chancellor Visit to India in 2026...
 Iran Nuclear Crisis and India’s Role f...
Iran Nuclear Crisis and India’s Role f...
 H1B Visa Program, Beneficiaries, Eligibi...
H1B Visa Program, Beneficiaries, Eligibi...




















