Table of Contents
Middle East Countries
The Middle East is a region of Western Asia and Northern Africa that has been a hub of international affairs for centuries. With its unique blend of history, cultures, and geopolitical importance, the Middle East is home to the world’s oldest civilisations and is extremely important because of its oil resources, trade routes, and religious landmarks. Comprehending the Middle East dynamics is critical for UPSC aspirants because it is a critical aspect of India’s foreign policy, energy security, and regional diplomacy.
Middle East Countries List with Capitals
The Middle East contains approximately 25 Countries, some of which include Iran, Iraq, and Israel. All Countries have capital cities, which include Tehran in Iran, Baghdad in Iraq, and Jerusalem in Israel, among others, and are vital centres of government and culture in the region.
| S. No | Country | Capital |
| 1 | United Arab Emirates | Abu Dhabi |
| 2 | Algeria | Algiers |
| 3 | Jordan | Amman |
| 4 | Turkey | Ankara |
| 5 | Greece | Athens |
| 6 | Iraq | Baghdad |
| 7 | Azerbaijan | Baku |
| 8 | Lebanon | Beirut |
| 9 | Egypt | Cairo |
| 10 | Syria | Damascus |
| 11 | Qatar | Doha |
| 12 | Pakistan | Islamabad |
| 13 | Afghanistan | Kabul |
| 14 | Sudan | Khartoum |
| 15 | Kuwait | Kuwait City |
| 16 | Bahrain | Manama |
| 17 | Oman | Muscat |
| 18 | Cyprus | Nicosia |
| 19 | Saudi Arabia | Riyadh |
| 20 | Morocco | Rabat |
| 21 | Yemen | Sanaa |
| 22 | Georgia | Tbilisi |
| 23 | Iran | Tehran |
| 24 | Libya | Tripoli |
| 25 | Tunisia | Tunis |
| 26 | Armenia | Yerevan |
Geopolitical and Economic Importance of the Middle East Countries
The Middle East is essential to international affairs due to the following reasons:
- Energy Resources: It holds approximately 48% of the oil reserves of the world, making it critical to world energy security.
- Strategic Location: The region dominates strategic sea chokepoints such as the Suez Canal, Strait of Hormuz, and Bab el-Mandeb.
- Religious Significance: It has significant places for Islam, Christianity, and Judaism, including Mecca, Medina, Jerusalem, and Bethlehem.
- Current Conflicts: International tensions, sectarian conflicts, and civil wars, like Syria, Yemen, and the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, render the area a hotbed of international diplomacy.
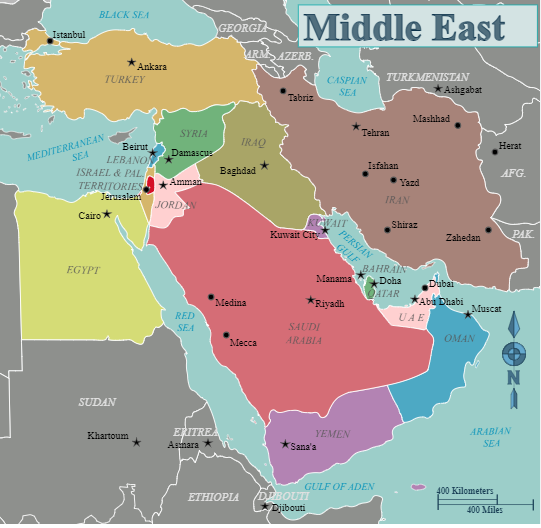
Middle East Countries Map
- Eastern Mediterranean coastlines (Syria, Israel, Lebanon)
- Arabian Peninsula (Oman, UAE, Yemen, Saudi Arabia)
- Gulf States (Bahrain, Qatar, Kuwait)
- The Red Sea, Persian Gulf, and Strait of Hormuz are vital for international trade routes and the supply of energy.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEE EC)
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEE EC) is a grandiose initiative to establish a contiguous, leak-proof transportation chain connecting India, the Middle East, and Europe. The corridor is of enormous geopolitical and economic importance, particularly with regard to India’s strategic importance and global value chain.
Key Components of the IMEE EC
- Railway Infrastructure: Building a rail system that links the Arabian Gulf to Europe and India to lessen the cost of shipping and time for goods.
- Digital Connectivity: High-speed internet cables to enhance digital connectivity throughout the region.
- Energy Infrastructure: Clean energy pipelines, such as hydrogen pipelines, as part of a green energy program.
- Sustainability: Use of renewable energy sources to minimise carbon footprints and facilitate environmentally friendly trade.
Benefits of the IMEE EC
- Improved Global Supply Chains: By linking India, the Middle East, and Europe through rail and sea links, the IMEE EC will enable quicker and more stable transit of products. This would minimise the reliance on conventional ocean routes, providing more efficient supply chains for both basic goods and energy supplies.
- Strategic Positioning: For India, being at the centre of the corridor is strategically beneficial. It will enhance India’s economic connectivity with Europe and West Asia, making it less dependent on China-predominant routes such as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- Economic Growth: The corridor is anticipated to create massive economic prospects, such as the creation of jobs in industries like logistics, infrastructure, energy, and digital connectivity.
- Food Security: For developing countries, particularly in Africa and Asia, this project enhances food security through an effective means of transporting agricultural products and other essential supplies.
- Green Energy and Sustainability: The integration of clean hydrogen pipelines in the corridor is part of moving towards green energy. The emphasis on sustainability is in accordance with the worldwide campaign to fight climate change.
Significance for India
- Strategic Connectivity: The IMEE EC enables India to circumvent potentially unstable areas such as the Suez Canal and Hormuz Strait, with a safe trade route available. It is vital for India’s Act West Policy and its greater strategic interests in West Asia.
- Economic Boost: It will enhance India’s export industries, especially in commodities such as textiles, pharmaceuticals, and manufactured products, by offering effective trade routes to Europe and the Middle East.
- Geopolitical Impact: Being a substitute for China’s BRI, the corridor increases India’s geopolitical standing so that it becomes a determining factor in the destiny of global trade routes.


 Geological Heritage Sites of India: Sign...
Geological Heritage Sites of India: Sign...
 Places in News for UPSC 2026 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2026 for Prelims...
 Lake Natron: Location, Features, Wildlif...
Lake Natron: Location, Features, Wildlif...

























