Table of Contents
Context: A new scientific paper by CSIR-NIO and INCOIS claims that Karnataka’s diversion of the Mahadayi River will have a limited ecological impact on Goa, sparking protests by local groups in Goa.
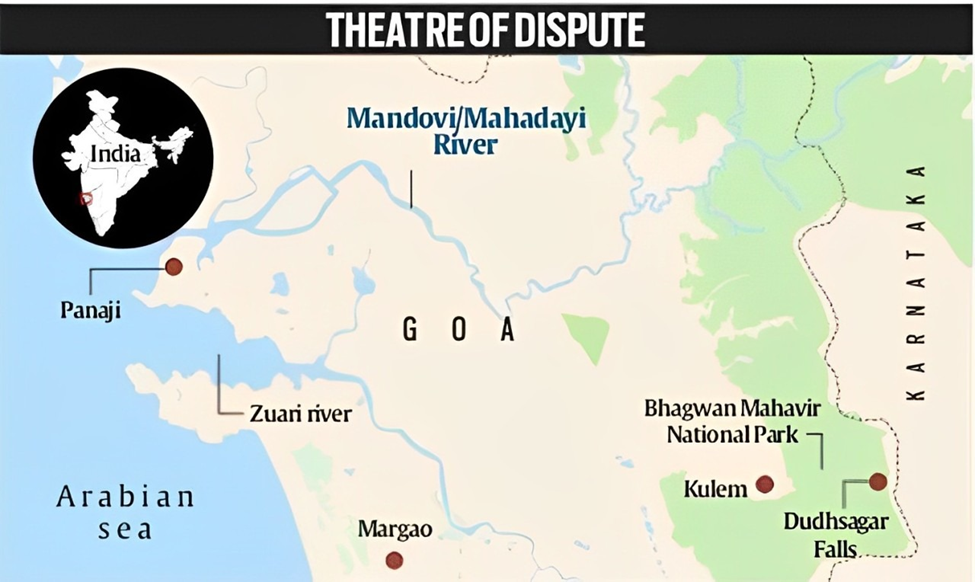
About Mahadayi River
The Mahadayi River, or the Mandovi River in Goa, and often referred to as Mhadei, is an important west-flowing river of India.
- Type: Rain-fed river.
- Origin: Bhimgad Wildlife Sanctuary, Belagavi district, Karnataka.
- Flows Through: Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Goa.
- Mouth: Arabian Sea near Panaji, Goa.
- Major tributaries: Kalasa, Banduri, Mapusa, Ragada, Nanuz, Valvoti, Nerul, St. Inez Creek, Dudhsagar.
Origin and Course of Mahadayi River
- The Mahadayi River has its origin in a group of around 30 springs at Bhimgad in the Western Ghats of the Belagavi district of Karnataka. There is the Bhimgad Wildlife Sanctuary here.
- It flows for a total distance of about 111 km.
- Its path passes through three states:
- Karnataka: 35 km
- Maharashtra: 1 km (an extremely short section)
- Goa: 76 km, where it is locally called the Mandovi.
Tributaries of the Mahadayi River
The Mahadayi River has several tributaries, including:
- Kalasa Nala
- Banduri Nala
- Mapusa River
- Nerul River
- St. Inez Creek
- Rio de Ourém
- Valvanti River
- Udnai River
- Dudhsagar River
- Ragada River
- Kotrachi Nadi
- Surla Nala
- Haltar Nala
- Singar Nala
- Doli Nala
- Irti Nala
- Bail Nadi
Significance of Mahadayi River
- Lifeline of Goa: Mandovi is the lifeline of Goa, offering drinking water to half of the population of the state.
- Agriculture: It sustains agricultural operations through irrigation.
- Ecology and Biodiversity: The river basin is high in biodiversity, which passes through the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and hotspot of biodiversity. It is home to different flora and fauna, such as endemic and endangered species occurring in sanctuaries like the Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary and Bhimgad Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Tourism and Navigation: The river is significant for navigation purposes, such as the transportation of iron ore. It is also helpful for tourism through the popular Dudhsagar Falls and river cruises, notably in Goa.
- Cultural Significance: The river and basin sustain diverse populations and are of cultural and historical significance.
| Mahadayi Water Dispute |
|


 Geological Heritage Sites of India: Sign...
Geological Heritage Sites of India: Sign...
 Places in News for UPSC 2026 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2026 for Prelims...
 Lake Natron: Location, Features, Wildlif...
Lake Natron: Location, Features, Wildlif...




















