Table of Contents
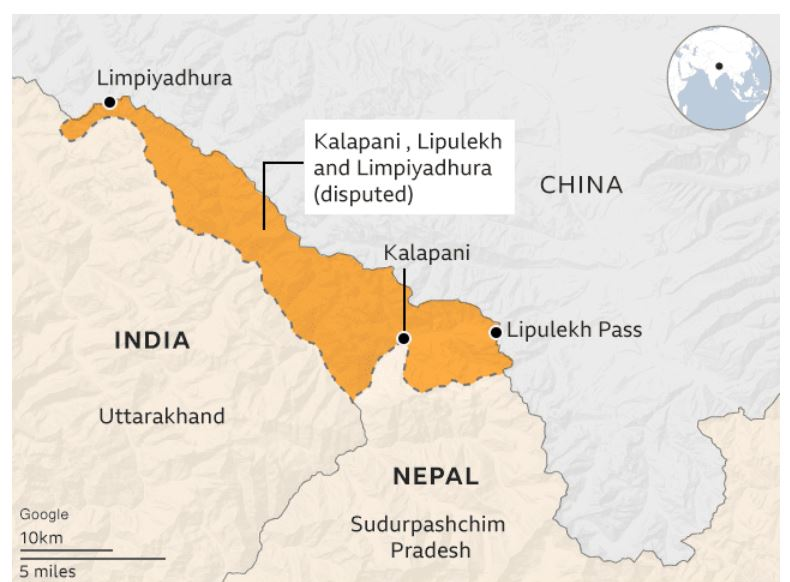
Context: Nepal has opposed the India-China decision to restart border trade through the Lipulekh Pass in Uttarakhand, calling it unexpected and unacceptable as the region is disputed (Kalapani-Lipulekh-Limpiyadhura).
Lipulekh Pass – Location and Features
- A high-altitude mountain pass in the Kumaon region of Uttarakhand, near the India–Nepal–China trijunction.
- Connects Uttarakhand (India) with Tibet (China).
- Altitude: ~5,334 m (17,500 ft).
- Acts as a gateway to the higher Himalayas due to its elevation and strategic location.
- First Indian border post opened for trade with China (1992).
- Later followed by Shipki La (Himachal Pradesh, 1994) and Nathu La (Sikkim, 2006).
Significance of Lipulekh Pass
- Ancient Trade Route
- Historically used as a key trade corridor linking India with the Tibetan plateau.
- Religious Importance
- Integral to the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra, a major Hindu pilgrimage route.
- Strategic Importance
- Located near the contested Kalapani-Limpiyadhura region, claimed by both India and Nepal.
- Serves as a vital border trade and military route in the Himalayan frontier.
Major Passes of Uttarakhand
Mana Pass
- Located in Uttarakhand on the border with Tibet.
- Elevation: 5610 m.
- Lies slightly north of the holy place Badrinath.
- Remains closed during winter (Nov–Apr).
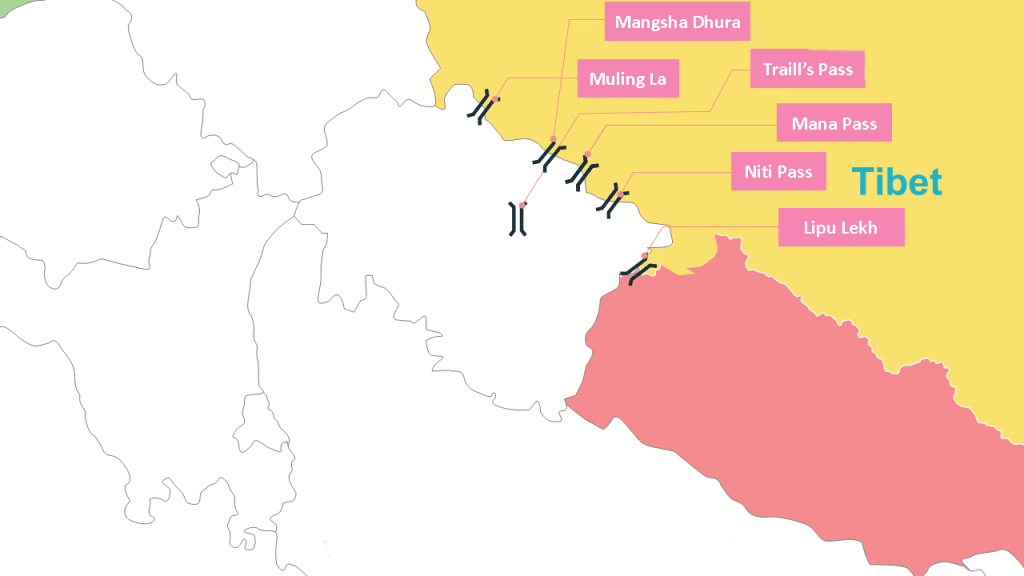
Mangsha Dhura
- Border pass between Uttarakhand and Tibet.
- Used by pilgrims on the route to Kailash–Mansarovar.
Niti Pass
- Border pass between Uttarakhand and Tibet.
- Remains closed during winter (Nov–Apr).
Muling La Pass
- Border pass between Uttarakhand and Tibet.
- Located north of Gangotri.
- Elevation: 5669 m in the Great Himalayas.


 Geological Heritage Sites of India: Sign...
Geological Heritage Sites of India: Sign...
 Places in News for UPSC 2026 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2026 for Prelims...
 Lake Natron: Location, Features, Wildlif...
Lake Natron: Location, Features, Wildlif...

























