Table of Contents
Context: PM Modi’s July 2024 address to Namibia’s Parliament symbolised India’s people-centric diplomacy: quoting local poets, invoking cultural symbols like the Welwitschia mirabilis (national plant) and Springbok, and using Oshiwambo phrases.
India-Namibia Relations: Three-Step Diplomatic Logic
Shared Historical Solidarities
- Evoking anti-colonial heritage and liberation struggles.
- India’s role in Namibia’s independence: hosting SWAPO’s first diplomatic office and Indian General Prem Chand commanding UN peacekeeping forces during the transition.
- Builds credibility of “long-haul” engagement vs. episodic Western presence.
Present Pragmatic Cooperation
- Bilateral trade: ~$800 million.
- India’s wider $12 billion development partnership across Africa.
- Key projects:
- India-Namibia Centre of Excellence in IT at NUST.
- “India Wing” at Ongwediva campus (funded by $12 million).
- Capacity-building in IT aligns with Namibia’s youthful, tech-ready population.
Future-Oriented Knowledge Partnerships
- Namibia: first African nation to adopt India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
- Potential transfer of not just digital tools but also India’s regulatory models and institutional design in tech governance.
- Signals rise of tech diplomacy as a pillar of South-South cooperation.
Namibia’s Strategic Importance for India
- Stability & Resources: Politically stable, rich in uranium and other minerals, with a growing tech base.
- Alignment in Vision: Namibian leadership echoes India’s calls for fairer global financial systems and South-South solidarity.
- Global South Role: Seen as a like-minded partner in reshaping international rules.
Gaps and Missed Opportunities
- Symbolism vs. Substance: First Indian PM visit in nearly 30 years produced only modest outcomes—two MoUs (entrepreneurship and health), Namibia joining Global Biofuels Alliance and CDRI.
- Critical Minerals Gap: Despite Namibia’s status as a top uranium producer, no concrete strategic framework on resource cooperation was finalised (e.g., value addition, workforce training, resilient supply chains).
- Consistency Problem: India’s Africa engagement has historically seen long gaps, raising concerns about sustained follow-through.
Namibia’s Significance for India
1. Strategic & Geopolitical Importance
- Gateway to Southern Africa: Namibia’s location offers India access to landlocked African nations via the Atlantic coast.
- Strengthening Global South Ties: Aligns with India’s focus on South-South cooperation and Africa outreach.
- Countering Chinese Influence: Partnership helps balance China’s growing footprint in African infrastructure and mining sectors.
2. Energy & Mineral Resources
- Uranium Supply: Namibia is a major exporter of uranium, critical for India’s civil nuclear program.
- Diamonds & Rare Minerals: A Potential source of strategic minerals needed for electronics and green tech.
- Energy Cooperation: Opportunities in green hydrogen, solar, and offshore energy.
3. Economic & Trade Potential
- UPI Expansion: India’s digital public infrastructure, like UPI, being introduced, boosts fintech diplomacy.
- Pharma & Healthcare: Namibia needs affordable medicines and healthcare services—India is a key partner.
- Investment & Skill Development: Scope for Indian investment in mining, agriculture, IT, and vocational training.
4. Defence & Maritime Collaboration
- Indian Ocean Security: Collaboration possible in maritime domain awareness and naval diplomacy.
- Defence Training & Equipment: Scope for defence exports and military training programs.
5. People-to-People & Diplomatic Relations
- First PM Visit in 27 Years: Signals renewed focus on Africa, especially the southern region.
- Educational Ties: Namibian students often study in Indian universities under scholarships and the ITEC program.
- Cultural Bonds: The Growing Indian diaspora and cultural exchanges foster goodwill.
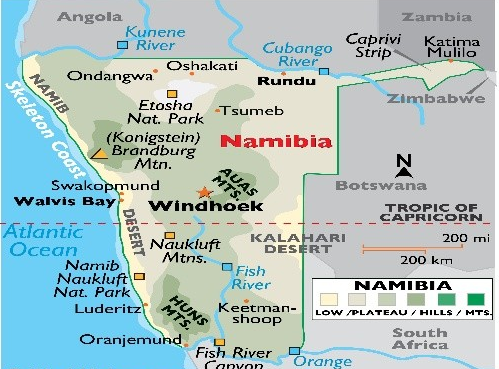
Geographical Overview of Namibia
- Location: Situated in southwestern Africa, Namibia has access to the Atlantic Ocean, making it a strategic gateway to inland African nations.
- Capital: Windhoek
- Neighbouring Countries: Shares borders with Angola, Zambia, Botswana, and South Africa; western boundary opens to the Atlantic Ocean.
Way Forward
- Beyond Symbolism: India needs consistent, institutionalised engagement, not episodic gestures.
- India-Africa Forum Summit: Upcoming summit could be a platform to:
- Formalise cooperation frameworks.
- Expand knowledge partnerships (digital, health, education).
- Secure critical minerals collaboration.
- Credibility Test: India’s role as a Global South leader depends not only on commitments but also on delivery, consistency, and inclusivity.


 German Chancellor Visit to India in 2026...
German Chancellor Visit to India in 2026...
 Iran Nuclear Crisis and India’s Role f...
Iran Nuclear Crisis and India’s Role f...
 H1B Visa Program, Beneficiaries, Eligibi...
H1B Visa Program, Beneficiaries, Eligibi...




















