Table of Contents
India has recorded a significant improvement in the Human Development Index (HDI) 2024, climbing to position 130 among 193 countries, as indicated in the most recent United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) report. This represents a consistent increase from last year’s position of 132, a reflection of improved healthcare, education, and incomes.
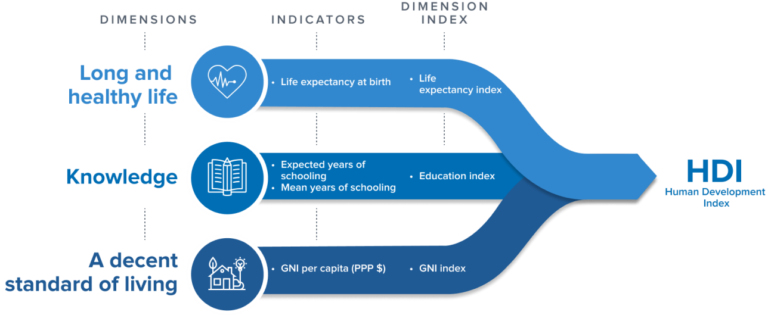
What is the Human Development Index (HDI)?
The HDI is a composite index that assesses a country’s average achievement in three basic dimensions of human development:
-
Health: Life expectancy at birth
-
Education: Mean years of schooling and expected years of schooling
-
Standard of Living: Gross National Income (GNI) per capita (PPP)
This index, developed by UNDP, provides a more holistic view of development beyond just economic growth.
Findings of Human Development Index (HDI)
1. Global HDI Trends
-
Switzerland retained the top position with the highest HDI value.
-
The global average HDI value has returned to pre-COVID levels after a dip during 2020–2021.
-
High-income countries recovered faster from pandemic setbacks compared to low- and middle-income nations.
-
The “Global North-South divide” in human development widened.
2. India’s Performance
-
Rank: 130 out of 193 countries (an improvement from 132 in 2023)
-
HDI Value: Increased to 0.644
-
Category: Remains in the Medium Human Development group
-
Life Expectancy: Rose to 72.0 years
-
Mean Years of Schooling: 6.9 years
-
Expected Years of Schooling: 13.1 years
-
GNI per capita (PPP): $9,047
3. South Asia Snapshot
-
India ranks higher than Bangladesh (133), Nepal (143), and Pakistan (164)
-
Sri Lanka (78) and Bhutan (125) rank above India
-
Afghanistan remains one of the lowest-ranked in the region
4. Inequality and Gender Development
-
Global Gender Inequality Index (GII) shows women lag in education, income, and political participation.
-
India’s GII rank improved from 108 to 102
-
Gender-based disparities and labor participation remain areas of concern globally and in India.
5. Emerging Concerns
-
Climate change, conflict, and economic shocks are key threats to human development progress.
-
More than 90 countries face stagnation or decline in HDI over the last five years.
-
Rising inequality within countries, despite overall HDI progress,s is a worrying trend
| Schooling | 13.0 years | 13.1 years |
| GNI per Capita (PPP) | $8,400 | $9,047 |
| Gender Inequality Index (GII) | 108 | 102 |
Why India’s Rank Improved: Major Drivers
1. Healthcare Initiatives
India’s life expectancy rose to 72 years, supported by schemes like:
-
Ayushman Bharat – PM-JAY: Largest health assurance scheme globally.
-
Mission Indradhanush: Widening vaccination coverage.
-
Nutrition Programs like Poshan Abhiyan addressing malnutrition.
2. Educational Advancements
-
Increase in school enrolment and NEP 2020 implementation boosted learning outcomes.
-
Government investment in Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan, DIKSHA, and PM SHRI Schools is paying off.
3. Economic Growth & Welfare Schemes
-
Rising GNI per capita due to digital growth, service sector expansion, and direct benefit transfers.
-
Schemes like PM Jan Dhan Yojana, MGNREGA, and Startup India enhanced economic inclusivity.
HDI Comparison with Neighbouring Countries (2024)
| Country | HDI Rank (2024) | HDI Category |
|---|---|---|
| India | 130 | Medium HD |
| Bangladesh | 133 | Medium HD |
| Nepal | 143 | Medium HD |
| Pakistan | 164 | Low HD |
| Sri Lanka | 78 | High HD |
| China | 75 | High HD |
| Bhutan | 125 | Medium HD |
India now ranks ahead of Bangladesh, Nepal, and Pakistan, but lags behind China and Sri Lanka.
Gender Inequality and Development: Progress & Gaps
While India’s Gender Inequality Index (GII) rank improved from 108 to 102, challenges remain:
-
Female labor force participation remains below 25%.
-
Despite more women in education and local governance, representation in Parliament and corporate leadership is still limited.
-
The recently passed Women’s Reservation Bill aims to strengthen political empowerment.
About Human Development Index
- The Human Development Index (HDI) assesses key aspects of human development beyond just income.
- It measures overall well-being, considering comprehensive criteria that account for more than financial status.
- The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) publishes the HDI.
Human Development Approach
- The index stems from the human development approach created by Mahbub ul Haq and is further influenced by Amartya Sen’s work on human capabilities.
- The HDI is framed around the ability of individuals to achieve desirable life outcomes.
Indicators
- Health Indicator: Life expectancy at birth is used to measure the health dimension of HDI.
- Education Indicators: The education dimension is assessed using two indicators:
- Expected years of schooling and
- Mean years of schooling.
- Living Standard Indicator: Gross National Income per capita, adjusted for purchasing power parity (PPP), evaluates the living standards.
| Related Information |
|


 Dynamic Pricing: What It Is and Why It's...
Dynamic Pricing: What It Is and Why It's...
 SSC MTS Salary 2025, Check Highest Salar...
SSC MTS Salary 2025, Check Highest Salar...
 F-35 Fighter Jet Stranded in Kerala: Dis...
F-35 Fighter Jet Stranded in Kerala: Dis...





















