Table of Contents
Context: Lotte Bjerre Knudsen won the Lasker Award for co-inventing GLP-1 drugs, which revolutionised treatment for diabetes and obesity.
What are GLP-1 Drugs?
- GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) is a natural hormone (incretin) released after eating.
- It helps regulate blood sugar, fat metabolism, and control appetite.
- GLP-1 receptor agonists are synthetic drugs that mimic GLP-1, activating similar responses in the body.
- Mostly administered through injections, though oral forms are being developed.
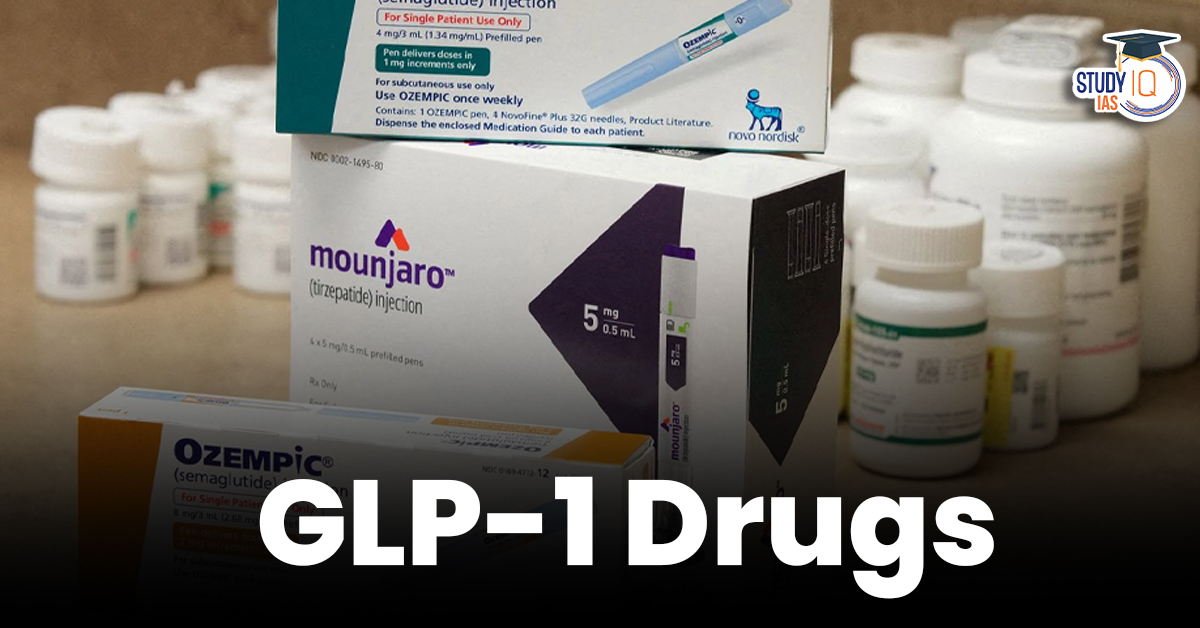
- Popular GLP-1 drugs include:
- Semaglutide (by Novo Nordisk)
- Tirzepatide (by Eli Lilly)
- Both are now available in India and are significantly improving diabetes and obesity treatment.
How Do GLP-1 Drugs Work?
- Stimulate insulin release when blood sugar is high.
- Inhibit glucagon secretion, lowering liver glucose output.
- Slow down gastric emptying, preventing sugar spikes.
- Suppress appetite, leading to reduced food intake.
- Tirzepatide also mimics the GIP hormone for a dual-action effect.
Genesis and Development
- Incretins were first mentioned in 1906, but gained attention post-insulin discovery in 1921.
- GLP-1 hormone was isolated in 1986.
- Early research in the 1990s showed potential, but the hormone was unstable.
- Novo Nordisk developed:
- Liraglutide (daily injectable)
- Semaglutide (weekly dose) offers better weight loss and fewer side effects with dose control.

 Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
 Ion Chromatography, Working and Applicat...
Ion Chromatography, Working and Applicat...
 Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...
Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...




















