Table of Contents
Context: A recent report titled ‘The State of the Haryana Aravallis: Citizens’ Report – Part 2’ has raised concerns about severe environmental degradation and a public health crisis caused by illegal dumping and burning of waste across the Aravalli range in Haryana.
About Aravallis
- The Aravalli Range is one of the oldest mountain ranges in the world, predating even the formation of the Himalayas.
- Geographical Spread: It is located in north-western India, stretching approximately 692 km in the states of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Haryana and Delhi.
Need to Save the Aravallis
- Ecological Significance: Home to diverse flora and fauna, including leopards, hyenas, and over 200 bird species.
- Climate Regulation: A critical role in India’s monsoon system, and helps in regulating temperature in the surrounding regions, like Delhi-NCR.
- The range acts as a natural barrier, preventing the Thar Desert from encroaching into the fertile agricultural lands of Rajasthan and Gujarat.
- Water Security: Essential for groundwater recharge and maintaining local hydrology.
- Air Quality: Serves as a green lung, significantly reducing air pollution in the region.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Supports numerous rare and endemic species, making it an ecologically valuable hotspot.
Severe Factors Responsible for Degradation
- Illegal Mining and Deforestation: Extensive extraction of minerals leads to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and loss of forest cover.
- Illegal Waste Dumping: Over 100 identified locations where solid, chemical, and industrial waste are illegally dumped, contaminating soil and groundwater.
- Waste Burning: Uncontrolled burning releases toxic chemicals and pollutants into the air, severely affecting public health and the environment.
- Weak Monitoring & Enforcement: Ineffective regulatory oversight facilitates illegal activities like waste disposal, mining, and encroachments.
- Urbanisation Pressure: Expansion of urban settlements, especially around Gurugram and Faridabad, is shrinking natural ecosystems.
Impacts of Aravalli Degradation
- Ecological and Biodiversity Loss: Reduction in habitat leading to declining wildlife populations (leopards, hyenas, bird species).
- Loss of native plant species, adversely impacting local biodiversity.
- Groundwater Contamination and Scarcity: Illegal waste dumping contaminates groundwater with heavy metals, pathogens, and toxic chemicals.
- Reduced groundwater recharge capacity due to deforestation and mining.
- Air Pollution and Public Health Crisis: Toxic emissions from waste burning cause respiratory diseases, allergies, cancers, and other health issues.
- Diminished air quality, particularly affecting Delhi-NCR.
- Increased Desertification and Climate Change Effects: Loss of forest cover accelerates soil erosion and desertification.
- Reduced ability to moderate temperatures, exacerbating heatwaves in surrounding urban areas.
- Socio-economic Consequences: Negative impact on agriculture and livestock due to contaminated water and soil degradation.
- Decline in tourism potential and associated economic losses.
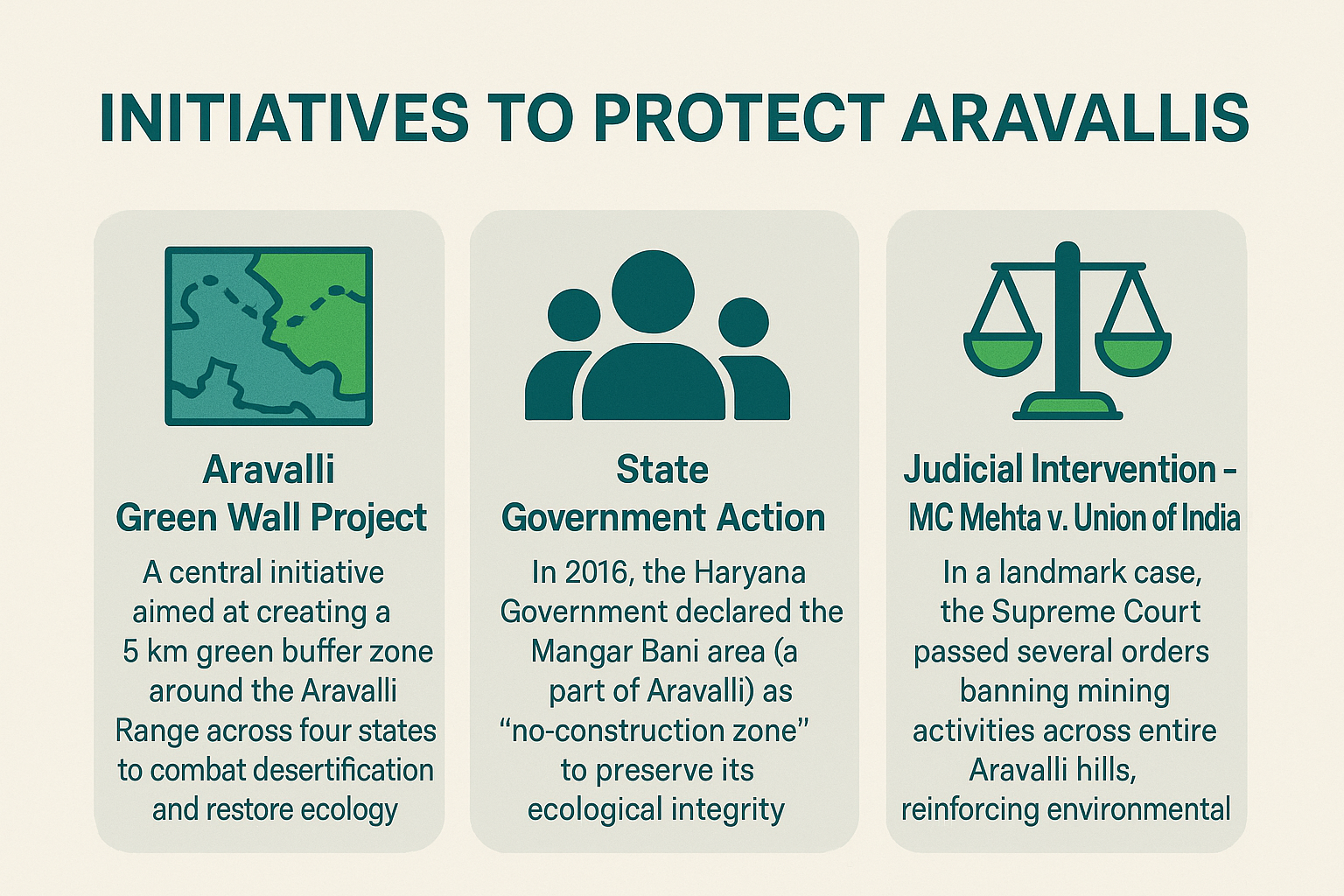
| Initiative/Project For Aravallis Restoration |
|
Proposed Solutions
- Legal Protection and ‘No-Go’ Zones: Declare the entire Haryana Aravalli range a ‘no-go’ zone for mining, dumping, burning of waste, and construction.
- Strengthened Monitoring & Accountability: Formation of an Aravalli Protection Task Force led by Deputy Commissioners and overseen by the Chief Secretary.
- Deploying 24/7 surveillance and drone monitoring, especially near state borders.
- Strict Implementation of Waste Management Rules: Enforce Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016, emphasising source segregation, composting, and recycling.
- Relocating Landfills: Shift existing landfills like Bandhwari away from ecologically sensitive zones to minimise contamination.
- Awareness and Community Engagement: Conduct independent environmental assessments.
- Engage local communities through education and incentives for sustainable practices and a strict ban on single-use plastics.


 Species in News for UPSC Prelims 2026: C...
Species in News for UPSC Prelims 2026: C...
 World Wetlands Day 2026: Theme, History,...
World Wetlands Day 2026: Theme, History,...
 Geological Heritage Sites of India: Sign...
Geological Heritage Sites of India: Sign...




















