Context: The Competition Commission of India has revised the definitions of various cost measures it will apply in assessing whether a company’s pricing of goods or services constitutes predatory pricing.
About Predatory Pricing
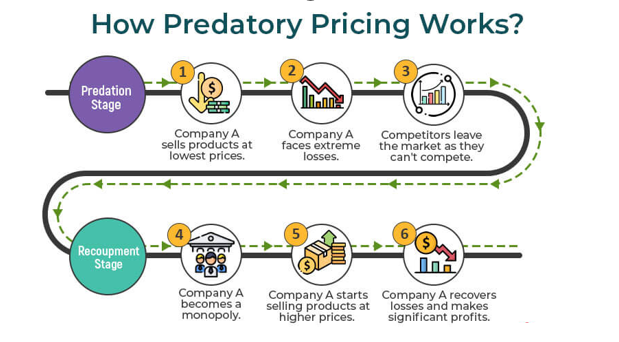
- Predatory Pricing is a form of anti-competitive behaviour where a company lowers its prices to drive out competitors and establish a strong market position.
- The goal is to eventually raise prices once the competition is weakened or removed.
- Predatory pricing is often used by large, established companies that can absorb short-term losses.
- Predatory pricing is illegal in India under Section 4, the Competition Act, 2002.
- It is illegal because it can create a monopoly and eliminate choice.
Competitive Pricing: It is a strategy where a company sets its prices in line with its competitors.
| Competition Commission of India (CCI) |
- Establishment: Formed in 2003 under the provisions of the Competition Act, 2002.
- Parent Ministry: Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- Body: Statutory body created to enforce the Competition Act, 2002.
- Composition: Chairperson + 6 Members (maximum).
- Appointment: All appointments are made by the Central Government.
- Qualification: Must be qualified to be a High Court judge
- or
- Have at least 15 years of professional experience in fields like international trade, economics, law, finance, management, public affairs, or other areas deemed relevant by the Central Government.
- Objective: Aims to promote and sustain a competitive environment in the Indian economy by engaging with stakeholders, the government, and international counterparts.
- Amendment – 2009: The Competition (Amendment) Act, 2009 led to the establishment of the Competition Appellate Tribunal (COMPAT) to hear appeals against CCI’s orders.
- COMPAT served as the appellate authority for CCI decisions until 2017.
- Revised Appellate Mechanism (2017): In 2017, COMPAT was replaced by the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT) as the appellate body for CCI orders.
Related Facts
The repeal of the Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Act, 1969 (MRTP Act), and the enactment of the Competition Act, 2002 were based on the Raghavan Committee’s recommendations. |
Sharing is caring!



 SEBI’s SWAGAT-FI Framework for Low-Ris...
SEBI’s SWAGAT-FI Framework for Low-Ris...
 Out-of-Pocket Health Expenditure, Reason...
Out-of-Pocket Health Expenditure, Reason...
 Treasury Bills (T-bills): RBI Cuts Holdi...
Treasury Bills (T-bills): RBI Cuts Holdi...




















