Table of Contents
Modern warfare is no longer decided only by weapons and troop strength. Energy security has emerged as a decisive factor in military superiority. Armies today depend heavily on electricity for surveillance systems, AI-enabled weapons, communication networks, cyber infrastructure, and autonomous platforms.
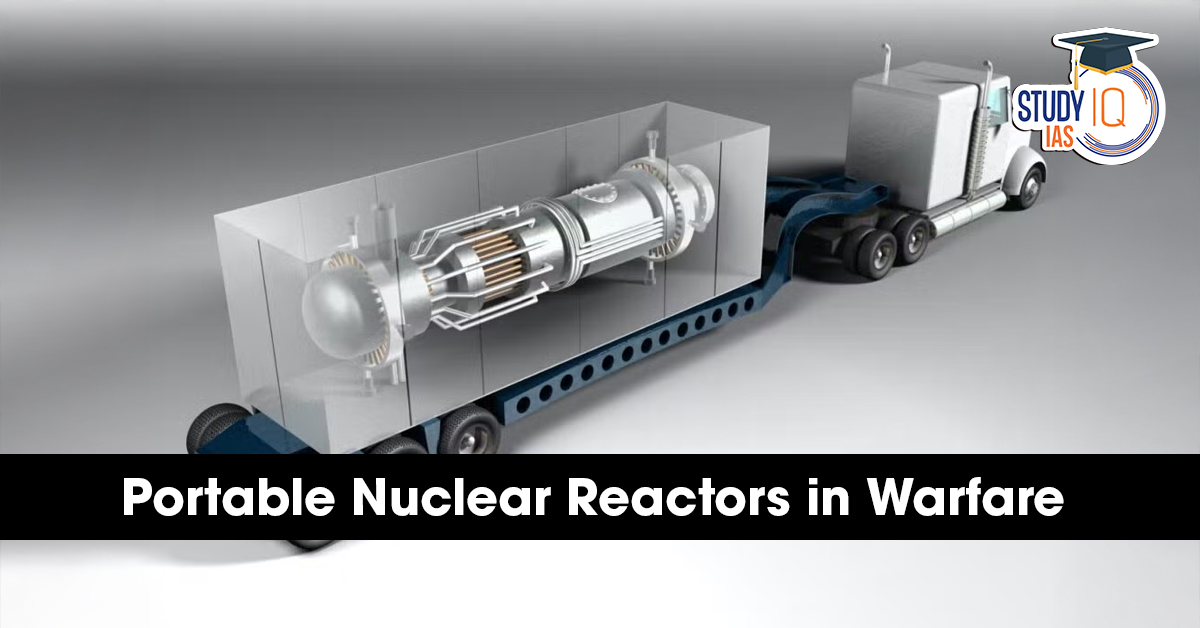
In this context, Portable Nuclear Reactors (Microreactors) are emerging as a revolutionary solution, offering reliable, long-duration, and logistics-independent power supply for military operations in remote and hostile environments.
What Are Portable Nuclear Reactors?
Portable nuclear reactors, often called microreactors, are ultra-small nuclear power systems designed for mobility and rapid deployment.
Key Features
-
Power Output: Typically 1–20 MW
-
Size: Comparable to a shipping container or truck-mounted unit
-
Deployment Time: Days or weeks (not years like large nuclear plants)
-
Operation Duration: Several years without refueling (in some designs)
Unlike traditional nuclear plants, these reactors are designed for plug-and-play energy deployment in extreme environments.
Why Militaries Need Portable Nuclear Energy
1. Reducing Fuel Logistics Vulnerability
Military bases currently depend heavily on diesel generators.
Fuel supply chains:
-
Are vulnerable to enemy attacks
-
Increase operational costs
-
Require continuous transport convoys
Microreactors can eliminate this vulnerability by providing long-term independent power.
2. Supporting High-Tech Warfare Systems
Modern warfare requires energy for:
-
AI-driven surveillance
-
Hypersonic weapon support systems
-
Quantum communication infrastructure
-
Directed energy weapons (future)
Portable nuclear reactors can provide stable baseload energy, unlike solar or wind.
3. Powering Remote and Harsh Deployments
These reactors are especially useful in:
-
Arctic military zones
-
High-altitude border areas
-
Desert warfare zones
-
Remote island bases
Strategic Advantages in Warfare
Continuous Power Supply
-
Works 24×7 regardless of weather
-
Higher reliability than renewables in combat zones
Rapid Deployment Capability
-
Can be transported by aircraft, ship, or heavy truck
-
Enables quick setup of forward bases
Enhanced Military Autonomy
-
Reduces dependence on vulnerable supply chains
-
Supports long-duration missions
Supports Future Warfare Technologies
-
AI command systems
-
Autonomous drone swarms
-
Electronic warfare platforms
Challenges and Risks
Nuclear Waste Management
-
Even small reactors produce radioactive waste
-
Long-term disposal solutions remain debated globally
High Initial Cost
-
Currently more expensive than diesel or renewables in some cases
Security Concerns
-
Risk of sabotage or capture in conflict zones
-
Requires high-level security protocols
Regulatory and Political Issues
-
Nuclear deployment laws differ across countries
-
Public acceptance challenges
Global Military Interest in Microreactors
Several countries are exploring military nuclear microreactors to:
-
Strengthen energy independence
-
Support overseas military bases
-
Maintain technological superiority
This reflects a broader shift where energy technology is becoming a strategic military asset, similar to missiles or cyber capabilities.
Implications for Future Warfare
Portable nuclear reactors may reshape military strategy by:
-
Enabling energy-independent battle zones
-
Supporting AI-driven military ecosystems
-
Reducing operational costs over long missions
-
Allowing permanent remote military presence
Future battlefields may see energy infrastructure as important as ammunition supply.
Relevance for India and Emerging Militaries
For countries with difficult terrains, portable nuclear reactors could help:
-
Border infrastructure in high-altitude regions
-
Remote island defense
-
Disaster-resilient military installations
However, adoption would require:
-
Strong nuclear safety frameworks
-
Waste management strategy
-
Public trust in nuclear technology
Conclusion
Portable nuclear reactors represent a transformative shift in military energy strategy. As warfare becomes more technology-driven, energy security will be as critical as weapons capability.
While cost, safety, and waste challenges remain, portable nuclear reactors are likely to play a crucial role in future military logistics, enabling energy-independent, technology-enabled, and strategically resilient armed forces.

 Ajnala Well Discovery: Rewriting Local H...
Ajnala Well Discovery: Rewriting Local H...
 Weaponisation of AI in Cybercrime: Threa...
Weaponisation of AI in Cybercrime: Threa...
 Herath Festival in Kashmir: Celebrations...
Herath Festival in Kashmir: Celebrations...




















