Table of Contents
India has successfully launched the much-anticipated NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) satellite aboard the GSLV-F16 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), Sriharikota. This marks a historic collaboration between ISRO and NASA, combining the expertise of both agencies to create one of the world’s most advanced Earth observation satellites. NISAR is expected to revolutionize climate science, disaster management, and environmental monitoring by delivering real-time, high-resolution data.
NISAR Satellite Launch Highlights – Live Updates
- 18:01 IST – ISRO confirms flawless cryogenic stage performance and satellite separation: “GSLV-F16 delivered NISAR to orbit.”
- 17:50 IST – Second stage separation completed; cryogenic third stage begins.
- 17:25 IST – Automatic launch sequence activated.
- 17:08 IST – 102nd launch from Sriharikota; 18th GSLV flight.
- 16:51 IST – Over a decade of development effort culminates in successful launch.
- 16:44 IST – Countdown initiated for launch at 5:40 PM.
- 16:13 IST – First 90 days reserved for in-orbit testing and calibration.
NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR)
The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) mission is a historic joint Earth-observing satellite mission between the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). The mission is one of the most prominent collaborations in space science between the two countries.
- Development: NISAR is a satellite jointly developed by NASA and ISRO for Low Earth Orbit (LEO) observation.
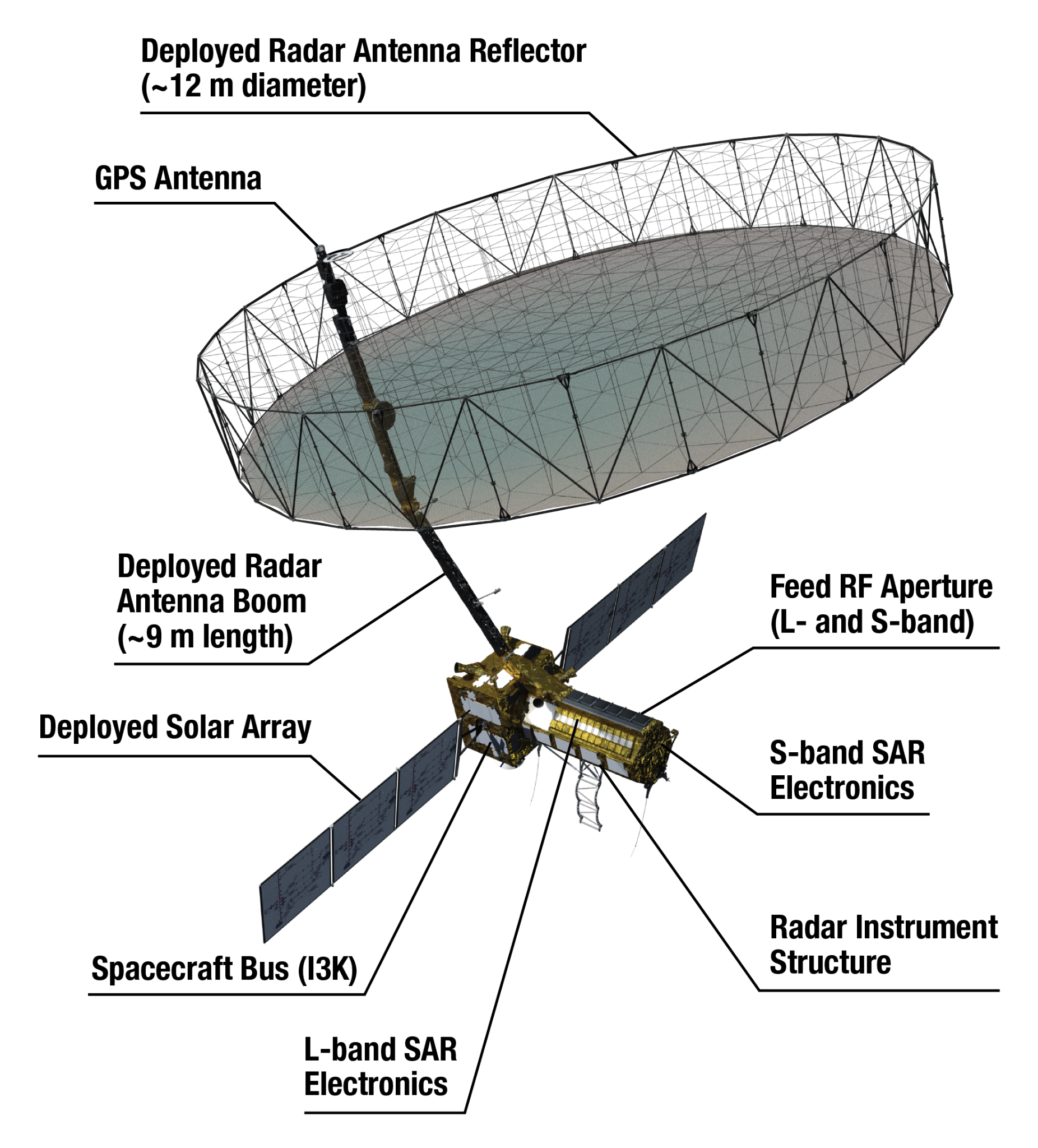
- Size and Weight: It is an SUV-sized satellite, weighing around 2,800 kilograms.
Details About NISAR Satellite
- Objective: To monitor tectonic movements, water bodies, water stress, vegetation cover, snow cover, and more.
- Earth Surface Monitoring: Tracks subtle changes in the Earth’s surface.
- Volcanic Eruptions: Spots warning signs of imminent volcanic eruptions.
- Groundwater Monitoring: Helps monitor groundwater supplies.
- Ice Sheet Tracking: Tracks the rate at which ice sheets are melting.
- Duration: 3 years.
Function
Can fully cover Earth in 14-15 days.
- Imaging Frequency: Captures images of Earth’s land, ice sheets, and sea ice every 12 days.
- Surface Movement Detection: Detects the earth’s surface movement as small as 0.4 inches over an area.
Features of NISAR Satellite
- Dual Frequency: Equipped with L-band and S-band radars.
- NASA Contribution: L-band radar, GPS, solid-state recorder, and payload data subsystem.
- ISRO Contribution: S-band radar, GSLV launch system, and spacecraft.
- Antenna Reflector: Features a large 39-foot fixed antenna reflector to focus radar signals emitted and received by the upward-facing feed on the instrument structure.
| Other Missions by ISRO |
Chandrayaan-4:
Spadex (Space Docking Experiment):
Gaganyaan Mission:
Sukhrayaan Mission:
|
New Application Areas for Satellites
- Bharatiya Antariksha Station: Planned space station with the first module launch targeted by 2028.
- New Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV): Named Surya, under development.
- Quantum Key Distribution Satellite: Aimed at secure communication.
- Software-Defined Radio Satellite: A communication satellite in development.
- Aircraft Monitoring Constellation (ADS): A satellite constellation to monitor all aircraft in Indian airspace and assist airport authorities in managing air traffic.


 Grammy Awards 2026: Full Winners List, H...
Grammy Awards 2026: Full Winners List, H...
 World Wetlands Day 2026: Theme, History,...
World Wetlands Day 2026: Theme, History,...
 Union Budget 2026 Highlights: Key Announ...
Union Budget 2026 Highlights: Key Announ...

























