Table of Contents
Context
- Russian President Vladimir Putin and North Korean leader Kim Jong-un signed a security pact in Pyongyang, promising mutual assistance in the event of aggression.
- The pact revives memories of the Cold War era, marking a significant shift in the geopolitical landscape.
Background
- Russia and North Korea were former allies during the Cold War.
- Both countries are currently under severe sanctions: Russia due to the Ukraine war and North Korea for its nuclear program.
- Both nations are at odds with Western countries and are seeking to bolster their alliance against the Western-led global order.
- Putin’s visit to Pyongyang, his first in 24 years, symbolises a new beginning in Russia-North Korea relations.
- Historically, Russia has supported international efforts to curb North Korea’s nuclear ambitions and has voted for UN sanctions against Pyongyang.
Recent Developments in Strengthening Ties Between Russia and North Korea
- The ongoing war in Ukraine has shifted Russia’s geopolitical strategies.
- As Western sanctions intensified, Russia sought support from North Korea, including ammunition and ballistic missiles.
- Following Kim Jong-un’s visit to Russia in September 2023, North Korea reportedly supplied ammunition to Russia.
- Mutual Support:
- Russia increased its supplies of food and fuel to North Korea.
- There is speculation that Russia might assist North Korea’s defence sector with critical technologies, although both nations deny any weapons trade.
- Strengthening Ties:
- The security pact elevates Russia-North Korea relations to a de facto alliance.
- This move is part of Putin’s broader strategy to expand Russia’s cooperation with countries opposed to the U.S.
- Russia has also engaged with Iran (buying kamikaze drones) and China (a key economic, technological, and energy partner).
Geopolitical Consequences
- By aligning with North Korea, Russia signals its intent to play a more significant role in Northeast Asia.
- North Korea, isolated and still technically at war with South Korea, gains substantial support from Russia.
- This alliance reduces North Korea’s incentive to negotiate denuclearization.
- Russia’s relationship with South Korea may deteriorate, and tensions with Japan could escalate further.
Regional and Global Implications:
- The pact could strengthen the emerging tripartite partnership in East Asia among Japan, South Korea, and the U.S.
- This development contributes to a new cold war dynamic between great powers, potentially leading to further geopolitical shifts.
Conclusion
- The Russia-North Korea security pact marks a significant shift in global alliances.
- Putin’s actions reflect his ambition to create an axis of countries opposed to the West.
- This alliance could reshape geopolitical strategies and alliances in Northeast Asia and beyond.
About Cold War Era
- The Cold War (1945-1991) was a period of geopolitical tension between the Soviet Union and its satellite states (Eastern Europe), and the United States with its allies (Western Europe) following World War II.
- The world was divided into two power blocs dominated by the Soviet Union and the US, engaging in an ideological war between capitalism (USA) and communism (Soviet Union).
- The term “Cold” is used because there was no direct large-scale fighting between the two sides, although they were involved in various proxy wars.
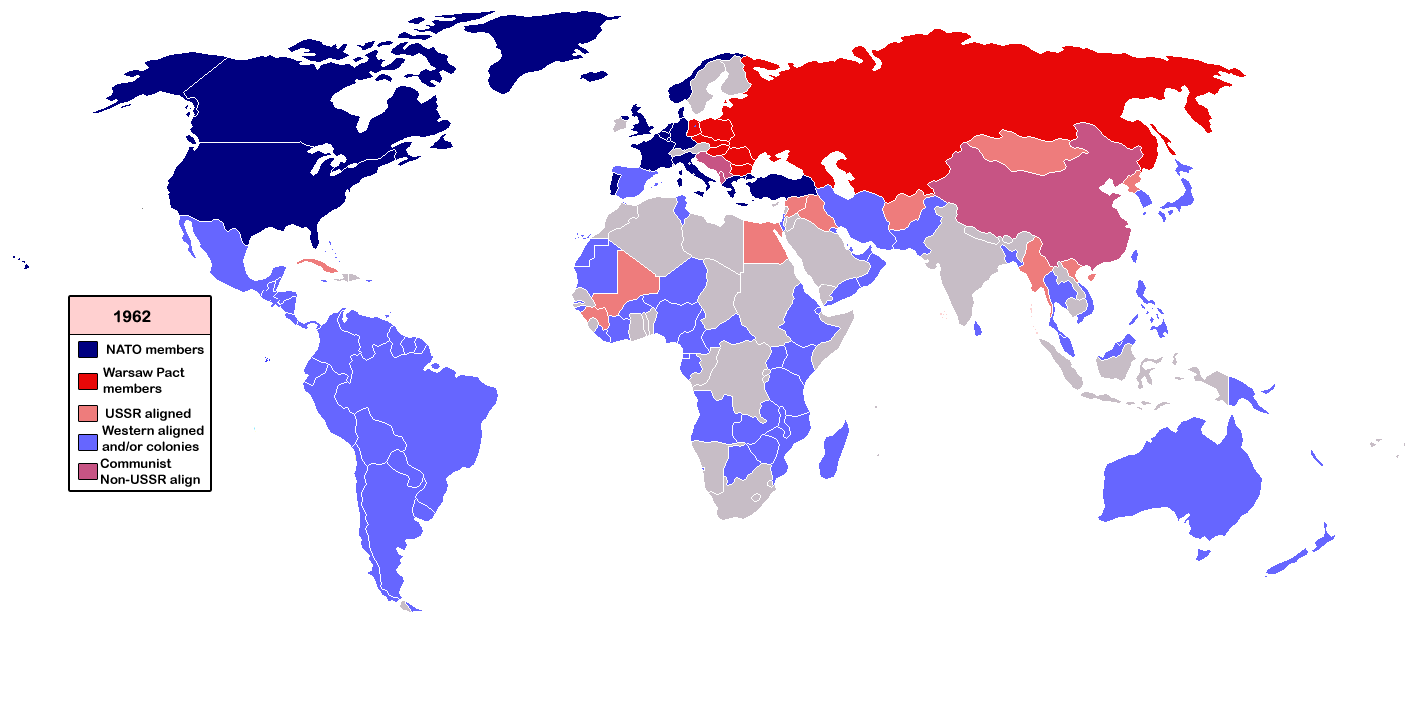
Superpowers and Alliances
- The US led the Western bloc, including allies such as the UK and France.
- The Soviet Union led the Eastern bloc, comprising Eastern European countries.
Soviet Union
- Officially known as the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), it was established in 1922 as the world’s first Communist state.
Reasons for the Cold War
- During World War II, the US, UK, and Soviet Union fought together against the Axis powers (Nazi Germany, Japan, Austria).
- Post-war, the wartime alliance dissolved due to conflicting interests and ideologies.
Key Event – Potsdam Conference (1945)
- Held in Berlin among the US, UK, and Soviet Union to discuss:
- Administration of defeated Germany.
- Demarcation of Poland’s boundary.
- Occupation of Austria.
- Role of the Soviet Union in Eastern Europe.
- Disagreements emerged:
- The Soviet Union wanted part of Poland as a buffer zone, which the US and UK opposed.
- The US did not disclose the atomic bomb’s nature to the Soviet Union, creating suspicion and embittering the alliance.
Key Characteristics
- Ideological Conflict: Between capitalist democracy (USA) and communist dictatorship (Soviet Union).
- Arms Race: Significant build-up of nuclear arsenals and military capabilities.
- Proxy Wars: Indirect conflicts in Korea, Vietnam, Afghanistan, and others.
- Espionage: Extensive spying and intelligence activities by both sides.
- Space Race: Competition for dominance in space exploration.


 Navigating Uncharted Waters: What Next f...
Navigating Uncharted Waters: What Next f...
 Astronaut Reentry Explained: How Spacecr...
Astronaut Reentry Explained: How Spacecr...
 Missile Interceptors Explained: Role in ...
Missile Interceptors Explained: Role in ...




















