Table of Contents
Context: Scientists at the University of Tasmania, Australia, have developed a portable ion chromatograph (Aquamonitrix).
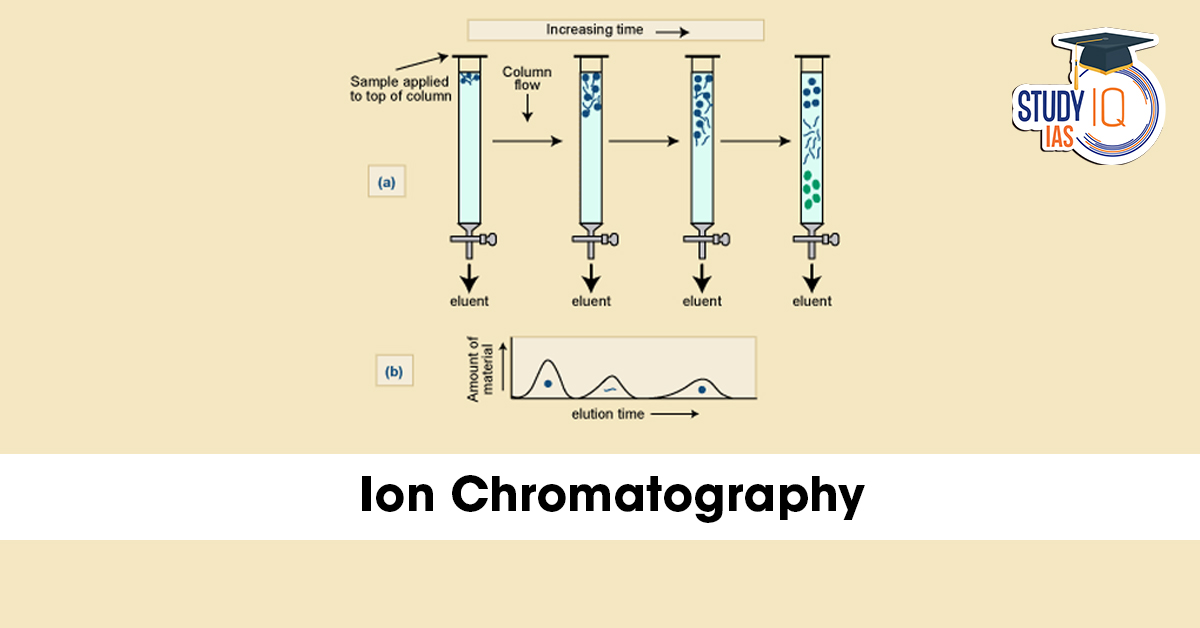
What is Chromatography?
Chromatography is a separation technique used to separate the components of a mixture based on their movement through a medium.
How it works
- Mixture (sample) is dissolved in a “mobile phase” (liquid or gas).
- Passed through a “stationary phase” (solid surface or column).
- Different components move at different speeds → get separated.
Applications
Used in
- forensics,
- pharmaceuticals,
- food safety,
- water testing, and
- chemical analysis.
What is Ion Chromatography (IC)?
- A special type of chromatography designed to separate and measure ions (charged particles) in a solution.
How it works
- Sample solution passes through a column filled with material that interacts with ions.
- Different ions (anions or cations) are separated based on how strongly they interact with the column.
- A detector (like UV absorbance) identifies and measures them.
Uses
- Detecting pollutants (nitrate, nitrite, fluoride, sulfate, chloride).
- Monitoring drinking water safety, soil chemistry, industrial processes, and environmental pollution.

 Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
 Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...
Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...
 Space Debris: Current State, Reasons, Im...
Space Debris: Current State, Reasons, Im...

























