Table of Contents
Context: The Reserve Bank of India has reported an improvement in the Financial Inclusion Index, which has risen to 67% in FY 2025, up from 64.2% in FY 2024.
What is Meant By Financial Inclusion?
- Financial inclusion refers to ensuring access to affordable financial products and services that cater to the needs of individuals and businesses responsibly and sustainably.
- It promotes entrepreneurship, drives business expansion, empowers women, and enhances risk management—ultimately strengthening economic activity, increasing productivity, and fostering overall economic growth.
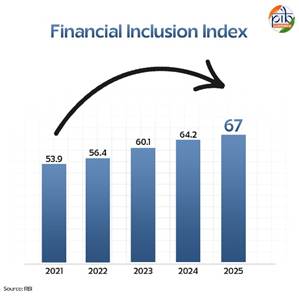
About the Financial Inclusion Index (FI-Index)
- The FI-Index is a composite measure designed to track the level of financial inclusion across India.
- Developed by the Reserve Bank of India in consultation with the Government and sectoral regulators (banking, insurance, pension, etc.).
- It covers five key sectors: Banking, Investments, Insurance, Postal Services, and Pensions.
- The FI-Index is published annually, every July, by the Reserve Bank of India.

Strategies for Financial Inclusion in India
- National Strategy for Financial Inclusion (NSFI) 2019–2024: Launched in 2019, it aims to remove barriers to accessing financial services and ensure inclusive participation.
- National Strategy for Financial Education (NSFE) 2020–2025: Aims to improve financial literacy, enabling individuals to make informed and responsible financial decisions.
- 5-C Approach to Achieve Strategic Objectives:
- Content: Develop relevant content and integrate financial education into school, college, and training curricula.
- Capacity: Build capabilities of intermediaries delivering financial services.
- Community: Utilise community-led models for spreading financial awareness.
- Communication: Design an effective communication strategy tailored to diverse audiences.
- Collaboration: Strengthen synergy among all involved stakeholders.
- 5-C Approach to Achieve Strategic Objectives:

Key Initiatives for Financial Inclusion
| Initiative | Objective |
| Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) | To provide basic banking services (savings, deposits, remittance, credit, insurance, pension) affordably to unserved and underserved citizens, enabling financial inclusion. |
| Centre for Financial Literacy (CFL) | To promote financial literacy through community-led, participatory methods for widespread financial inclusion. |
| Digital Banking Units (DBUs) | To offer digital banking services (account opening, fund transfers, loans, etc.) through physical units at the last mile. |
| Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY) | To provide affordable accident insurance (death/disability) to poor and underprivileged sections of society. |
| Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY) | To provide affordable life insurance cover to broader population including poor and rural citizens. |
| Atal Pension Yojana (APY) | To ensure old-age security by providing guaranteed pension especially to workers in the unorganised sector. |
| Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY) | To provide easy credit (up to ₹20 lakhs) to small/micro enterprises and entrepreneurs, promoting self-employment. |
| Stand Up India Scheme (SUI) | To promote entrepreneurship among SC/ST and women by supporting greenfield enterprises through loans and handholding support. |
| Unified Payments Interface (UPI) | To enable seamless, real-time digital payments and fund transfers for individuals and merchants, accelerating digital financial inclusion. |
| Mahila Sammriddhi Yojana (MSY) | To empower women from weaker sections by providing skill development, formation of self-help groups, and easy group loans. |
| Kisan Credit Card (KCC) | To provide timely and affordable credit to farmers for agricultural and allied activities, reducing dependence on informal sources. |
| Nationwide Campaign for Financial Inclusion (2025) | To saturate coverage of financial inclusion schemes at panchayat/urban local levels, covering new account openings, re-KYC, enrolments for insurance/pension, and awareness on digital fraud and grievance redressal. |
Challenges of Financial Inclusion in India
- Digital Divide: Limited access to smartphones, internet, and digital infrastructure in rural/remote areas restricts the reach of digital financial services.
- Low Financial Literacy: Many individuals, especially in rural and low-income groups, lack the knowledge to use banking and digital platforms effectively.
- Product Inaccessibility: Available financial products often do not match the unique needs of low-income or informal sector workers.
- Infrastructure Bottlenecks: Inadequate power supply, poor internet connectivity, and lack of last-mile delivery systems hinder access.
- Dominance of Cash Economy: A significant portion of the economy still operates in cash, especially in rural and informal sectors, resisting digital adoption.
- Cost Barriers: NEFT, RTGS, mobile wallet charges, and minimum balance requirements make banking costly for low-income groups.
- Lack of Trust in Digital Platforms: Fear of fraud, data breaches, and low awareness of grievance redressal mechanisms create hesitation in digital adoption.
- Dependence on Physical Bank Branches: Many banks still rely on physical presence for basic services like account opening, limiting access in rural and underserved areas.
- Informal Lending Dominance: A large section of the population continues to rely on unregulated moneylenders due to lack of formal credit access.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Digital Infrastructure: Expand internet connectivity, provide affordable smartphones, and promote public Wi-Fi in rural areas.
- Promote Financial Literacy: Launch targeted awareness programs using local languages, visual tools, and community-led models to improve understanding of financial services.
- Develop Customized Products: Design financial products tailored for informal sector workers, women, small farmers, and low-income households.
- Subsidize Transaction Costs: Remove or reduce charges on low-value transactions (like NEFT, UPI, wallets) and ensure no-frill, zero-balance accounts.
- Encourage Mobile-First Banking: Promote simple and secure mobile apps for banking, integrated with features like cash flow tracking and voice assistance.
- Build Consumer Trust: Enforce strong consumer protection rules, data privacy norms, and transparent grievance redressal systems.
- Digitize Core Banking Services: Enable full digital onboarding using Aadhaar and biometrics, reducing the need for physical branch visits.
- Promote Open Banking Ecosystem: Implement a well-regulated open banking framework to foster innovation, enable data portability, and increase access to credit for small borrowers.
- Improve Credit Delivery: Expand micro-credit and small-ticket loans through credit guarantee schemes and alternate data (like utility bills) for credit scoring.
- Link Government Schemes with Financial Access: Strengthen integration of DBT, PMJDY, APY, and insurance schemes with financial inclusion strategies to widen coverage.


 Out-of-Pocket Health Expenditure, Reason...
Out-of-Pocket Health Expenditure, Reason...
 Treasury Bills (T-bills): RBI Cuts Holdi...
Treasury Bills (T-bills): RBI Cuts Holdi...
 Fisheries Sector in India, Current Statu...
Fisheries Sector in India, Current Statu...

























