Context: The launch of the Axiom-4 Mission to the International Space Station (ISS) will be from the Kennedy Space Centre in Cape Canaveral, Florida.
How Astronauts Reach International Space Station (ISS)?
Pre-launch Preparation
Astronauts undergo rigorous training and preparation.
- Scientists select a precise time slot when the spacecraft trajectory aligns with the International Space Station (ISS) orbit.
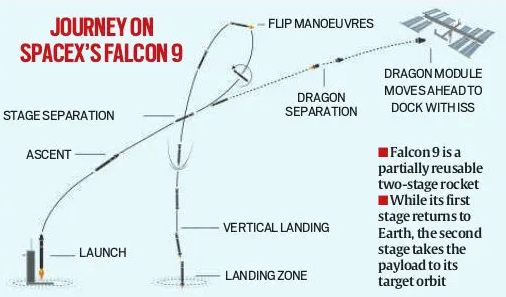
- Astronauts board the Crew Dragon spacecraft, attached atop the Falcon 9 rocket at Kennedy Space Centre, Florida.
Launch and Ascent
- The Falcon 9 rocket lifts off vertically.
- The first stage (booster) propels the spacecraft through Earth’s dense atmosphere, powered by 9 Merlin engines.
- Around the edge of space (~80-100 km altitude), the first stage separates and returns to Earth for reuse.
- The second stage (single Merlin engine) continues to propel the Dragon capsule into orbit.
Orbital Insertion
- After reaching orbit, the Dragon spacecraft separates from the second stage.
- The spacecraft initially enters an elliptical (oval) orbit slightly below the ISS orbit (~200-250 km altitude).
Rendezvous and Orbit Raising
Over the next several hours, the Dragon performs orbital raising manoeuvres.
| Journey Duration |
|
Approach and Docking
- As Dragon nears the ISS (within ~200 meters), it enters the “keep-out sphere“, a safety zone around the ISS.
- Autonomous Docking: Dragon aligns itself using GPS, cameras, and laser-based Lidar sensors, enabling precise positioning.
- The spacecraft gently moves toward the docking port on the ISS, matching speed precisely, effectively stationary relative to the ISS.
Docking and Hatch Opening
- After successful docking, the spacecraft is secured and undergoes thorough safety checks (~1-2 hours).
- Once cleared, hatches between Dragon and ISS open, allowing astronauts to enter the space station.


 Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
 Ion Chromatography, Working and Applicat...
Ion Chromatography, Working and Applicat...
 Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...
Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...

























