Context: A study by the International Labour Organization (ILO), released in Geneva has found that forced labour generates illegal profits worth $36 billion per year.
Key Findings of the Forced Labour-ILO Report
| Definition of Forced Labour |
| The ILO defines forced labour as involuntary work enforced through coercion or threats at any employment stage. |
- Dominance of Sexual Exploitation: Sexual exploitation constitutes $173 billion, three-fourths of total profits from forced labour, as reported by the International Labour Organization (ILO).
- Increase in Profits: A 37% surge in forced labour profits since a decade ago, with an increase of $64 billion as per 2021 ILO figures.
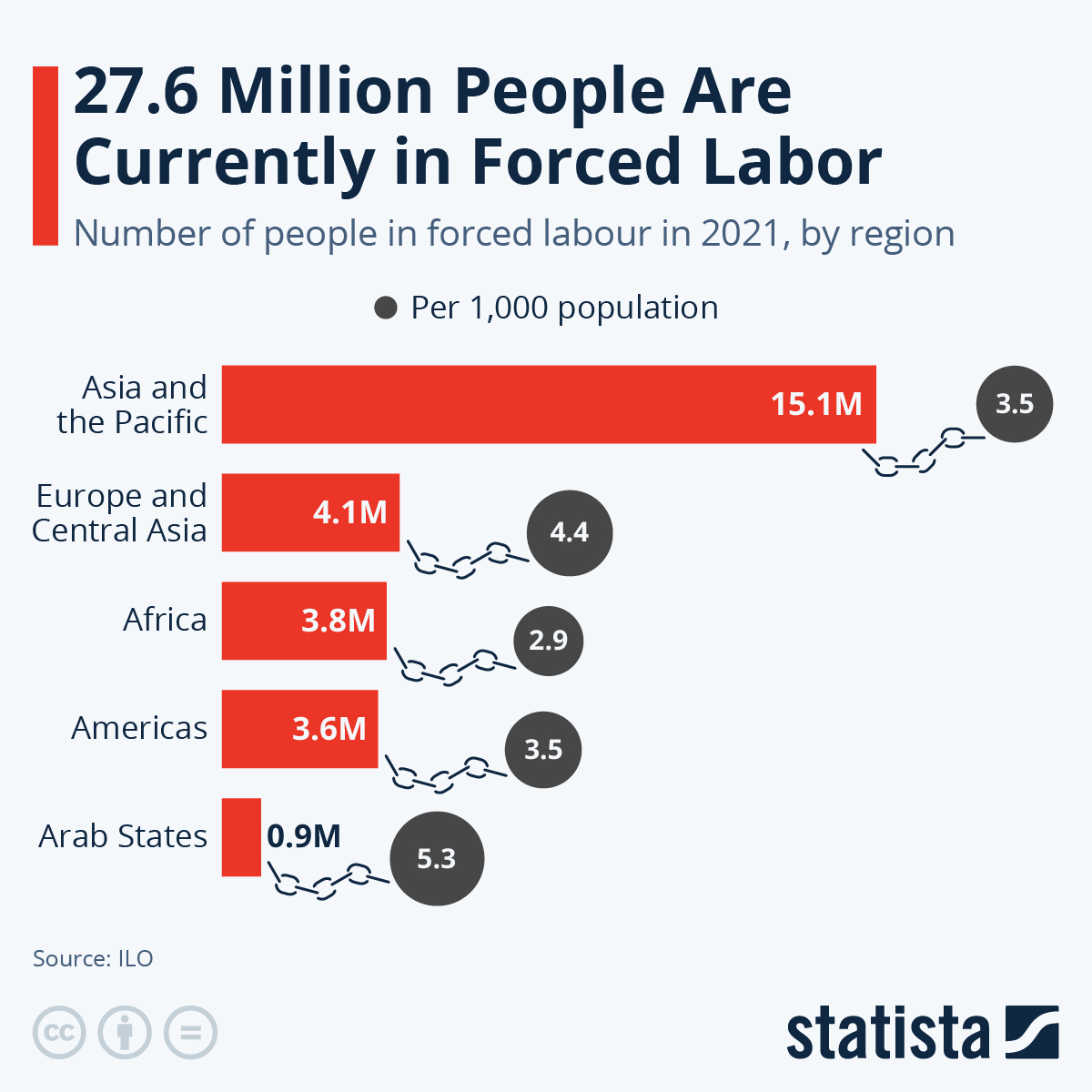
- Global Prevalence: On a typical day in 2021, around 27.6 million people were in forced labour, a 10% increase from five years earlier.
- Victims of Forced Labour: Out of these, 6.3 million, predominantly girls and women, suffered forced sexual exploitation, with children over one-quarter.
- Geographical Spread: Over half of forced labour occurs in the Asia-Pacific region, with Africa, the Americas, and Europe-Central Asia each hosting about 13-14%.
- Types of Forced Labour: Private sector forced labour accounts for 85%, including slavery, serfdom, bonded labour, and exploitative begging.
- Profit Distribution by Sector: The industry sector makes $35 billion, services nearly $21 billion, agriculture $5 billion, and domestic work $2.6 billion in illicit profits.
- Efforts and Challenges: Despite global efforts to eliminate forced labour, progress is insufficient to meet the UN goal of eradication by 2030.


 Effectiveness of Tobacco Taxation in Ind...
Effectiveness of Tobacco Taxation in Ind...
 Private Sector Participation in Defence ...
Private Sector Participation in Defence ...
 India–France Strategic Cooperation in ...
India–France Strategic Cooperation in ...




















