Context: Over 1.6 lakh people globally have undergone Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS), a medical procedure used to treat various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
What is Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)?
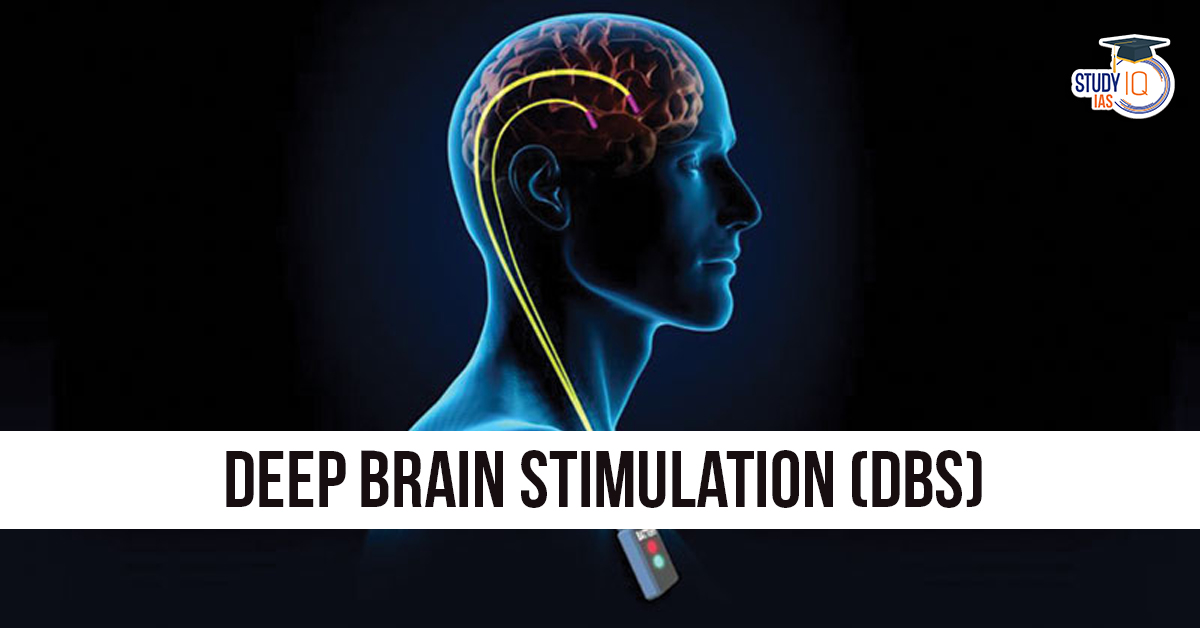
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a medical procedure where electrodes are implanted into specific areas of the brain.
- Used to treat neurological and psychiatric disorders by modulating brain activity.
How DBS Works
- Electrodes are connected by wires to a small pulse-generating device (like a pacemaker) implanted in the chest.
- This device sends mild electrical impulses to targeted brain regions.
- The stimulation helps correct abnormal brain signals or chemical imbalances.
Applications of DBS
- Primarily used for movement disorders, especially:
- Parkinson’s disease
- Essential tremor
- Dystonia
- Also approved for:
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Currently being studied for:
- Severe depression
- Epilepsy
Mechanism
- DBS modifies the way neurons communicate by delivering electrical signals.
- Interrupts faulty or erratic brain signals, reducing symptoms like:
- Tremors
- Muscle stiffness
- Involuntary movements
Advantages of DBS
- Non-destructive: Unlike brain surgeries that destroy tissue, DBS is reversible.
- If the device is turned off, stimulation stops immediately.
- Helps restore normal function at both the cellular and network levels in the brain.

 Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
 Ion Chromatography, Working and Applicat...
Ion Chromatography, Working and Applicat...
 Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...
Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...

























