Table of Contents
Orsk
Context
- Russia has evacuated around 2,000 people from their homes in the Russian city of Orsk after rising waters in the Ural river flooded riverside villages and caused a dam to burst.
- The water levels in Orsk, Russia prompted warnings about potential additional flooding.
- Additionally, the rising waters pose a threat to the southern part of Orenburg, where a “federal emergency” has been declared due to the Ural River’s overflow.
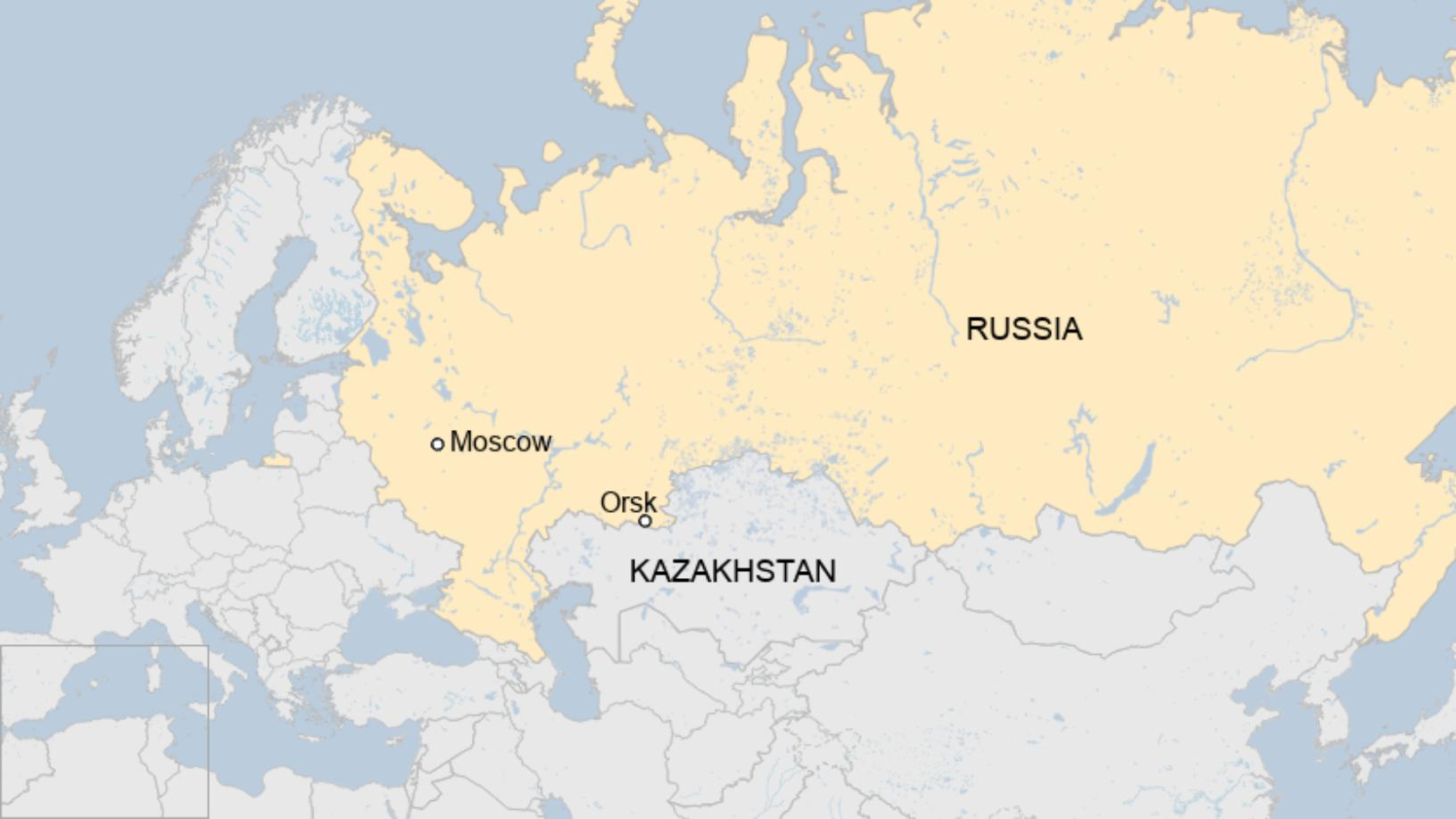
Mapping- Orsk
- Location and Geography: South-western Russia
- Second largest city in Orenburg Oblast, Russia
- Located on the steppe, 100 km southeast of the Ural Mountains
- Straddles the Ural River (border between Europe and Asia)
- Significance:
- Near the Kazakhstan-Russia border
- Emerged as an industrial centre by the 1930s due to natural resources.
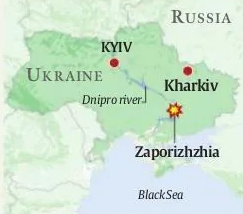
Zaporizhzhia
Context: Ukraine had attacked the Russian-controlled Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant three times.
About Zaporizhzhia
- Zaporizhzhia is a city located in southeastern Ukraine, on the banks of the Dnieper River.
- The Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant is the largest nuclear power plant in Europe and one of the ten largest in the world.
- The Zaporizhzhia Nuclear power plant was occupied by Russian forces in 2022.
VVPATs
Context: The Supreme Court announced that petitions for 100% verification of Voter Verified Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT) slips would be considered, ahead of the first phase of voting on April 19.
More in News
- The Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR) petitioned for cross-verification of Electronic Voting Machine (EVM) tallies with VVPATs in March 2023, suggesting barcodes on VVPAT slips for efficiency.
What is VVPAT?
- VVPAT machines, connected to EVMs, print a slip showing the voter’s choice, which is visible behind a glass window for seven seconds before being stored securely.
- The system is designed to enhance voter confidence by providing a physical audit trail of electronically cast votes.
Evolution and Adoption of VVPATs
- Initiated in 2010, VVPATs were introduced to make EVM-based voting more transparent.
- Following trials and political feedback, the Election Commission (EC) approved VVPAT design in 2013, amending the Conduct of Elections Rules for implementation.
- VVPATs saw first use in Nagaland in 2013, reaching 100% adoption by June 2017.
Current VVPAT Counting Process
- Based on the Indian Statistical Institute’s (ISI) recommendation, VVPAT slips from five randomly selected polling booths per Assembly constituency are counted.
- This process was mandated by the Supreme Court in 2019, increasing from the previous one polling station per constituency.
Legal Battles over VVPAT Verification
- The Supreme Court ruled in favour of VVPATs for election transparency in Subramanian Swamy vs Election Commission of India, leading to government funding for VVPAT implementation.
- A 2019 petition by Chandrababu Naidu sought a minimum of 50% VVPAT verification; however, the EC argued against it due to potential result delays and infrastructure challenges.
- EC’s Stance on 50% VVPAT Counting: Counting VVPAT slips is time-consuming, with EC citing an hour per station for matching slips with EVM counts, predicting significant delays in result announcement if increased.
- Infrastructure and manpower are cited as constraints against expanding VVPAT slip counting.
Political Demand for Increased VVPAT Verification
- Opposition parties argue for broader VVPAT verification to ensure voting transparency, ranging from demands for 50% to 100% verification.
- The INDIA alliance, including major opposition parties, demanded 100% VVPAT slip verification in December and sought a meeting with the Chief Election Commissioner.
Examples, Data and Case Studies For Value Addition
- Government initiative, Agriculture (GS 2, GS 3): Farmers in Rajasthan’s Shekhawati region are employing solar power for running electrical appliances and polyethene houses for drip irrigation.
- These methods have improved crop yields and incomes, with one farmer’s annual profit reaching ₹15 lakh due to organic farming with vermicompost.
- Additionally, the region is experiencing a substantial increase in the area of crops, nearly 3.5 times due to innovative practices and government subsidies for horticulture.
- Increased income from agriculture is evident, with the annual turnover of the ‘bakra mandi’ (goat market) in Sikar reaching ₹600 crore.
- Fundamental Rights, Judiciary, Climate Change (GS 2, GS 3): The Supreme Court of India has broadened the scope of the Constitution’s Articles 14 and 21, emphasising the protection of lives and livelihoods against climate change impacts.
- The Court has historically viewed environmental protection as integral to fundamental rights, as seen in the landmark M C Mehta v Union of India case (1987).


 Graphic Processing Units (GPUs) – Work...
Graphic Processing Units (GPUs) – Work...
 Gold Imports and the Indian Economy – ...
Gold Imports and the Indian Economy – ...
 Nilgiri Tahr Conservation: Ecology, Habi...
Nilgiri Tahr Conservation: Ecology, Habi...




















