Table of Contents
Green Revolution in Maize
Context: The Green Revolution in Maize helped in increased production.
Green Revolution in India
- Bengal Famine of 1943: The famine led to the death of approximately 4 million people in eastern India due to hunger.
- Pre-Green Revolution Efforts: Post-independence, the government focused on expanding farming areas, but food production lagged behind the growing population.
- Green Revolution Introduction: The Green Revolution introduced modern methods and technology, including HYV seeds, tractors, irrigation, pesticides, and fertilizers.
- Funding: The initiative was funded by the US, Indian Government, Ford Foundation, and Rockefeller Foundation.
- Wheat Revolution: The Green Revolution is often termed the Wheat Revolution, as wheat production increased by over three times between 1967-68 and 2003-04, while cereal production doubled.
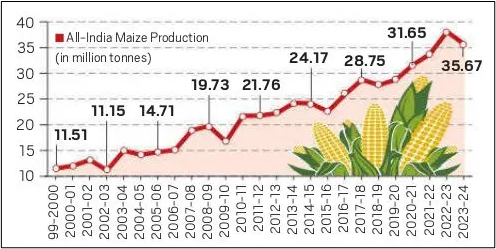
Maize Production Growth: Fact
- Tripling of Output: Between 1999-2000 and 2023-24, India’s maize production increased from 11.5 million tonnes (mt) to over 35 mt.
- Yield Improvement: Average per-hectare yields rose from 1.8 to 3.3 tonnes.
Usage of Maize
- Human Consumption: Only a fifth of maize production is used directly for human consumption.
- Animal Feed: Around 60% of maize is used as feed for poultry and livestock, indirectly consumed as chicken, eggs, or milk.
- Industrial Purposes: 14-15% of maize is used for industrial purposes due to its high starch content.
- Industrial Applications:
- Maize starch is utilised in textiles, paper, pharmaceuticals, food, and beverages.
- Maize is used as a feedstock for ethanol production, especially during the sugarcane off-season, due to a government shift from using surplus rice.
Innovations in Maize Varieties
- Waxy Maize Hybrid: IARI developed India’s first “waxy” maize hybrid, Pusa Waxy Maize Hybrid-1, with high amylopectin starch content suitable for ethanol production.
- Starch Recovery and Yield: The hybrid has a starch recovery rate of 68-70% and an average grain yield of 7.3 tonnes per hectare, with a potential of 8.8 tonnes.
- Field Trials: IARI partnered with the UP Distillers’ Association for field trials.
Advances in Maize Breeding Techniques
- Doubled Haploid Facility: CIMMYT established a maize doubled haploid (DH) facility in Karnataka, producing genetically pure inbred lines.
- Efficiency Improvement: The DH technology accelerates breeding, creating uniform lines in two cropping cycles.
- High-Yield and Tolerance: The facility produced 29,622 DH lines focusing on high-yielding, drought-tolerant, heat-tolerant, and pest-resistant varieties.
Role of the Private Sector
- Private Sector Involvement: Over 80% of maize area in India is planted with private sector-bred hybrids, unlike wheat and rice, which saw public sector dominance.
- Hybrid Yields: Private sector hybrids offer higher yields but are limited to the first generation.
- Collaborations: CIMMYT collaborates with public institutions and private companies like Mahyco, Shriram Bioseed, and Advanta Seeds.
Conclusion
- The maize production revolution has been significant but underappreciated in Indian agriculture.
- Sustaining and enhancing maize growth requires continued focus on innovation and collaboration.
RBI’s State of the Economy
Context: Recently the RBI article has been prepared by the RBI Deputy Governor Michael Patra and other central bank officials.
Key Highlight of the Article
- The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) article highlights concerns about the persistent accumulation of food price pressures and its impact on overall inflation, wages, rent, and inflation expectations.
- The article argued that food price shocks are not transitory, as evidenced by the experience over the past year.
Inflation and Policy Response
- The RBI has been cautious about higher food inflation potentially derailing the disinflation path.
- The RBI has kept the repo rate unchanged at 6.5% for the last 16 months due to concerns over food inflation.
| Repo Rate |
| The repo rate is the rate at which the RBI lends money to banks for short-term funding. |
- Spillover Effects: Food price pressures threaten the inflation outlook through spillovers to wages, rents, and inflation expectations.
- Headline Inflation: Year-on-year (y-o-y) headline inflation increased to 5.1% in June 2024 from 4.8% in May.
- Month-on-Month Increase: The increase was due to a positive momentum of 269 basis points (bps) in food, 6 bps in fuel, and 12 bps in the core group (excluding food and fuel).
- Food Inflation: Food inflation (y-o-y) rose to 8.4% in June from 7.9% in May.
- High-Frequency Data: By July 12, 2024, cereal prices, driven by wheat, and pulses prices, driven by gram and arhar/tur, registered increases.
- Edible oil prices, especially mustard and groundnut oils, also increased.
Persistent Food Price Shocks
- Non-Transitory Shocks: The article emphasises that food price shocks are not transitory based on the past year’s experience.
- Vegetable Prices: Persistent components and sporadic spikes in vegetable prices contribute to enduring inflation in this category.
Impact on Inflation Expectations
- Households’ Expectations: While households’ current perception of inflation has been moderating, their three-months-ahead and one-year-ahead expectations remain elevated.
- Core and Fuel Inflation: Gains in lowering core and fuel inflation are undermined by persistent food price inflation.
Economic Growth and Domestic Demand
- Strong Growth Momentum: Despite geopolitical headwinds and supply chain pressures, the Indian economy sustained strong growth momentum.
- Robust Domestic Demand:
- High-Frequency Indicators: E-way bills grew by 16.3% (y-o-y) in June 2024, with growth in both inter- and intra-state movements.
- Toll Collections: Increased by 37.4% (y-o-y) in June 2024.
- Automobile Sales: Grew by 18.2% (y-o-y) in June 2024, led by two-and-three wheelers, followed by passenger vehicles, though entry-level vehicle growth remained weak.
- Tractor Sales: Reached an eight-month high in June 2024, with total volumes surpassing the one-lakh mark, indicating improved farm sentiments and rural spending.
Positive Developments
- Agriculture Outlook and Rural Spending: The improvement in the agricultural outlook and revival of rural spending are highlighted as bright spots in demand conditions.
California Law on Gender Identity
Context
- California has become the first U.S. state to prohibit schools from sharing information about students’ gender identity and sexual orientation without the students’ consent, including with their parents.
- The policy is part of the Support Academic Futures and Educators for Today’s Youth Act, or the SAFETY Act.
Support and Opposition
- Supporters’ Viewpoint: Hailed as progressive legislation protecting the privacy of LGBTQIA+ youth.
- Critics’ Viewpoint: Argue that parents have the right to know about their children’s activities at school.
- Legal Challenge: A Southern California school district sued Governor Newsom, arguing against the law.
Key Provisions of the SAFETY Act
- Reasoning: Emphasises the importance of letting students decide when and to whom to disclose their gender identity.
- Personal Decision: The Act states that decisions regarding gender identity are deeply personal, impacting health, safety, and relationships.
| Legal Precedents |
| Chico Unified School District: In July 2023, a U.S. District Court Judge upheld the policy of not disclosing students’ gender identities to their parents, affirming the students’ right to privacy. |
Specific Clauses
- Clause (f): Policies requiring outing students without consent violate their rights to privacy and self-determination.
- Clause (g): Pupils have a constitutional right to privacy concerning sensitive information, affirmed by courts.
- Clause (d): LGBTQ+ youth thrive with parental support but can be harmed if forced to share their identities prematurely.
- Clause (e): Forcibly outing students removes opportunities for trust-building and readiness for conversations about identity.
Obligations Under the SAFETY Act
- State Department of Education:
- Develop or update resources for supporting LGBTQIA+ students and their families.
- Collaborate with families and relevant stakeholders.
- Provide resources like anti-bullying policies, counseling services, and suicide prevention policies.
- Protection for Employees:
- Officials and employees must not retaliate against staff acting according to the law.
- Schools and employees are not required to disclose students’ gender identity or sexual orientation without consent unless mandated by state or federal law.
Debate and Political Context
- Governor’s Spokesperson: The law protects the child-parent relationship by preventing inappropriate intervention by politicians and school staff.
- Opposition’s Argument: Lawyer Emily Rae argues that parents have a constitutional right to know what their children are doing at school, and schools should not keep secrets from parents.
- Polarised Reactions: The issue reflects broader political divisions, with Republican states restricting discussions on LGBTQ+ matters and Democratic states promoting greater visibility of diverse gender and sexual identities.
Examples, Case Studies and Data
- Economy (GS 3): Recently, the NITI Aayog report titled “Electronics: Powering India’s Participation in Global Value Chains” was released
- Importance of Global Value Chains (GVCs):
- GVCs account for 70% of international trade.
- Electronics represent 75% of GVC exports.
- Sector Growth:
- India’s electronics sector reached USD 155 billion in FY23.
- Production nearly doubled from USD 48 billion in FY17 to USD 101 billion.
- Mobile Phones as a Growth Driver:
- Mobile phones constitute 43% of electronics production.
- 99% of smartphones are manufactured domestically.
- Market Share and Capabilities:
- India holds only 4% of the global electronics market.
- Focus primarily on assembly with limited design and component manufacturing capabilities.
- Global Market and Exports:
- The global electronics market is valued at USD 4.3 trillion.
- India exports about USD 25 billion annually.
- Future Projections:
- Electronics manufacturing could reach USD 278 billion by FY30 in a Business As Usual scenario.
- Potential to generate 3.4 million jobs and USD 111 billion in exports.
- Targets and Requirements: To achieve a target of USD 500 billion by FY30:
- USD 350 billion from finished goods.
- USD 150 billion from components.
- Requires substantial policy support and strategic interventions.
- Strategic Focus Areas:
- Enhance production in mobile phones.
- Expand into wearables, IoT devices, and automotive electronics.
- Improve components manufacturing.
- Importance of Global Value Chains (GVCs):


 Graphic Processing Units (GPUs) – Work...
Graphic Processing Units (GPUs) – Work...
 Gold Imports and the Indian Economy – ...
Gold Imports and the Indian Economy – ...
 Nilgiri Tahr Conservation: Ecology, Habi...
Nilgiri Tahr Conservation: Ecology, Habi...




















