Table of Contents
Context: NITI Aayog released its report “Chemical Industry: Powering India’s Participation in Global Value Chains”
Status of Chemical Industry in India
Size & Contribution:
- India is the 6th largest chemical producer in the world and 3rd in Asia.
- Contributes over 7% to India’s GDP; accounts for ~13% of total industrial output.
- Employs over 2 million people.
- India’s share in the global chemical value chain: ~3.5%.
- Chemical trade deficit: USD 31 billion (2023) due to high dependence on imports, especially for speciality chemicals and feedstock.
Potential:
- Rapid growth in demand for speciality and green chemicals.
- Government targets a $1 trillion chemical sector by 2040, aiming for 12% global value chain share.
- Expected to generate significant exports and skilled jobs with focused interventions.
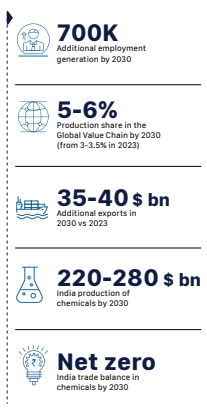
Vision for 2030:
- Target: 5-6% share in global chemical value chain, double current production, net-zero trade deficit, USD 35-40 billion extra exports, and 7 lakh new skilled jobs.
- Modern clusters, advanced tech adoption, regulatory streamlining, robust talent pool.
Challenges Facing the Indian Chemical Sector
- High Import Dependence: Heavy reliance on imported feedstock and speciality chemicals; limited domestic backward integration.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Outdated chemical clusters, and inadequate port and logistics infrastructure lead to higher costs than global competitors.
- Low R&D Investment: R&D spending only 0.7% (global average 2.3%), restricting innovation in high-value chemicals.
- Regulatory Delays: Lengthy and opaque environmental clearance processes stifle agility and add compliance burden.
- Talent Shortages: 30% shortfall in skilled professionals, especially in emerging areas like green chemistry, nanotech, and safety.
- Fragmented Industry: A large number of small, fragmented players with low economies of scale.
Solutions / Interventions Proposed by NITI Aayog
- World-Class Chemical Hubs: Upgrade and build new clusters; empower central committee and dedicated chemical fund for shared infrastructure.
- Strengthen Port & Cluster Infrastructure: Develop high-potential clusters; improve port infrastructure with advisory chemical committees.
- Opex Subsidy Scheme: Incentivize incremental production, import substitution, and export-oriented production through targeted subsidies.
- Boost R&D and Technology Access: Allocate more funds for R&D; foster industry-academia partnerships; acquire advanced tech via global tie-ups.
- Fast-Track Regulatory Approvals: Simplify and accelerate environmental clearance; enhance transparency and accountability.
- Strategic FTAs: Negotiate FTAs with specific provisions for the chemical sector; improve exporter awareness and utilization.
- Skill Development: Expand ITIs and specialized institutes; upgrade faculty; promote industry-relevant curriculum and training.


 SEBI’s SWAGAT-FI Framework for Low-Ris...
SEBI’s SWAGAT-FI Framework for Low-Ris...
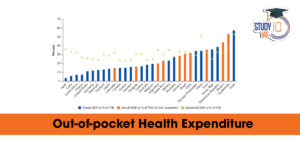 Out-of-Pocket Health Expenditure, Reason...
Out-of-Pocket Health Expenditure, Reason...
 Treasury Bills (T-bills): RBI Cuts Holdi...
Treasury Bills (T-bills): RBI Cuts Holdi...

























