Context: The University of Jyväskylä in Finland has recently detected and successfully measured the half-life of the heaviest known proton-emitting isotope of astatine, ¹⁸⁸At.
About Astatine Element
General Properties
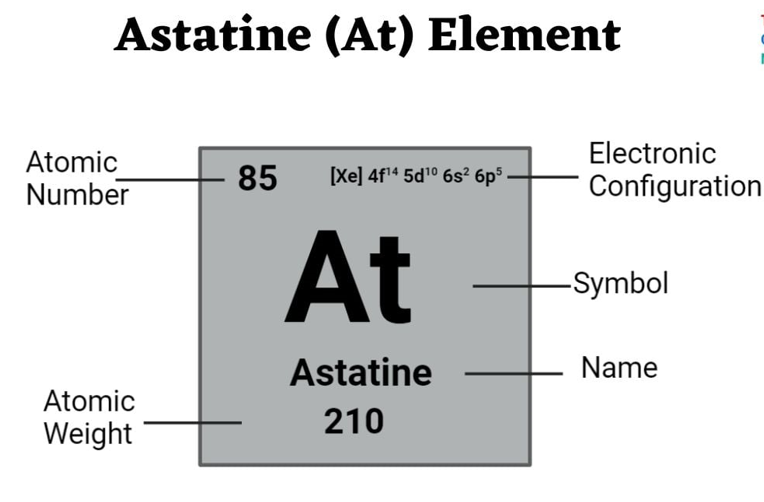
- Symbol & Atomic Number: At, atomic number 85
- Category: Halogen group (Group 17)
- Appearance: Likely a dark-colored solid at room temperature and pressure
- Radioactivity: Highly radioactive; emits a blue glow due to ionising the surrounding air
- Isotopes: 41 known radioactive isotopes, ranging from mass numbers 188 and 190 to 229
Chemical & Physical Properties
- Chemical Behaviour: Resembles iodine but exhibits more metallic characteristics
- Compounds: Forms compounds similar to iodine but with more metallic properties
- Electronegativity: Estimated to be between 2.2 and 2.5
- Density: Estimated to be around 6.3 g/cm³
- Melting Point: Estimated to be between 302°C and 337°C
- Boiling Point: Estimated to be between 337°C and 352°C
Uses
- Medical Applications: Used in targeted alpha-particle cancer therapy
- Astatine is released in the human thyroid; hence, it is used in the treatment of thyroid diseases.
- Research: Studied for potential use in radiopharmaceuticals
- Industrial Applications: Limited due to its rarity and radioactivity
| Fact |
| The total amount of astatine in the Earth’s crust at any time is less than 30 grams, with only a few micrograms ever artificially produced. |


 Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
 Ion Chromatography, Working and Applicat...
Ion Chromatography, Working and Applicat...
 Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...
Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...




















