Table of Contents
Context: The NPA rate of loans under the Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) for Scheduled Commercial Banks has increased to 9.81% in March 2025 from 5.47% in March 2018.
In April 2025, the PM Mudra Yojana will complete 10 years of its launch. In 10 years, 52 crore loans worth ₹32.61 lakh crore were sanctioned.
About Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY)
Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) was launched in 2015, for providing loans up to Rs. 10 lakh to the non-corporate, non-farm small/micro-enterprises.
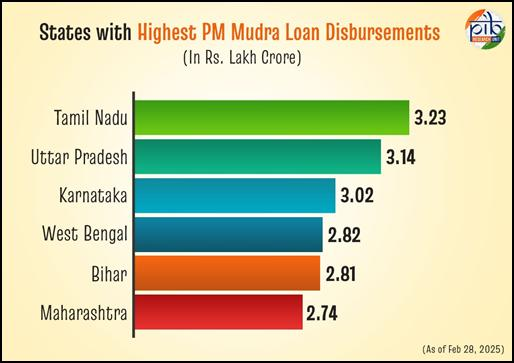
A Decade of Growth with PM Mudra Yojana
Ever since it was introduced in April 2015, the Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) has disbursed more than 52 crore loans worth ₹32.61 lakh crore, creating a national entrepreneurial wave. Growth of business is no longer limited to metros—now it is reaching small towns and villages, where first-time entrepreneurs are seizing the reins of their own destiny. The shift in mindset is evident: people are no longer job seekers; they are becoming job creators.

Funding Provision
- MUDRA stands for Micro Units Development & Refinance Agency Ltd., is a financial institution set up by the Government.
- These loans are given by Commercial Banks, RRBs, Small Finance Banks, MFIs and NBFCs.
- MUDRA does not lend directly to micro-entrepreneurs/individuals.
- Three products are created under MUDRA, as per the stage of growth and funding needs of the beneficiary micro unit.
- Shishu: up to ₹ 50,000.
- Kishore: ₹ 50,000 – ₹ 5 lakh.
- Tarun: ₹ 5 lakh – ₹ 10 lakh.
- Tarun Plus: ₹10 lakh – ₹20 lakh (It would be available to entrepreneurs who have availed and successfully repaid previous loans under the Tarun category).
- The guarantee coverage loans for amounts up to ₹20 lakh will be provided under the Credit Guarantee Fund for Micro Units (CGFMU).
- CGFMU is a government-backed initiative aimed at providing credit guarantee coverage to loans extended to micro-enterprises and small businesses.
- Established in 2015, this fund is managed by the National Credit Guarantee Trustee Company Ltd. (NCGTC).
- Loans under the MUDRA scheme are collateral-free loans.
Key Features of Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY)
| About Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) | |
| PMMY Launch |
|
| Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana Objectives |
|
| PMMY Eligibility |
|
| Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana Loans |
|
| Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana Sectors Covered |
|
Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana Loans
- Public sector banks: Public sector banks accounted for almost 46 per cent of all Mudra loans disbursed in value terms till June 30 this year. For them, bad loans during the seven years stood at 98 per cent of their disbursements.
- Private sector banks: They account for 36 per cent of the value of loans disbursed under the scheme, but they have far better recovery than public sector banks. For them, bad loans during the seven years stood at just 1.32 per cent of their disbursements.
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs): In terms of the value of loans disbursed, they account for 06 per cent of the total, and their NPAs are at about 4.22 per cent.
- Small Finance Banks: Accounted for 27 per cent of total disbursement, and their NPAs stood at 2.79 per cent.
Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana Benefits
- In terms of the number of loan accounts, private banks catered to 10.46 crore beneficiaries or almost 53 per cent of the total 19.78 crore loan accounts.
- On the contrary, public sector banks covered just 4.66 crore beneficiaries, or under 24 per cent of the total Mudra loan accounts.
- The share of private sector banks is very high in Shishu category loans, while the share of public sector banks is high in Tarun category loans.
What are Non-Performing Assets (NPA)
- Non-Performing Assets (NPA) a loan or advance for which the principal or interest payment remains overdue for a period of 90 days.
- Classification (as per the RBI guidelines):
- Substandard assets: Assets which have remained NPA for a period of less than or equal to 12 months.
- Doubtful assets: An asset that has remained in the substandard category for a period of 12 months.
- Loss assets: It is considered “uncollectible” or of such little value that its continuance as a bankable asset is not warranted, although there may be some recovery value.
- Metrics that help us to understand the NPA situation of any bank:
- Gross NPA: It refers to the total NPAs of the banks.
- Net NPA: Net NPA is calculated as Gross NPA -Provisioning Amount.
- i.e. Net NPA gives the exact value of NPAs after the bank has made specific provisions for it.
| What is Provisioning? |
Special Mention Accounts (SMA)
|

Conclusion
Over the past decade, Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana has always proved the potential of financial inclusion and the resilience of grassroots innovation. Prior to 2014, credit was typically accessible to those who were well-connected, whereas small entrepreneurs encountered obstacles such as complicated paperwork or had to turn to informal finance. Banks gave out irresponsible loans to large corporates, whereas legitimate borrowers lost access to credit. MUDRA filled this void with a cleaner, inclusive option that provided a level playing field to all.
With more than 52 crore loans approved, the scheme has empowered women, SC/ST/OBC groups, and rural entrepreneurs by increasing access to formal credit. The increase in average loan size, an increasing proportion of MSME credit, and the transition from micro to small enterprises indicate its increasing influence. PMMY is not only driving self-employment and employment generation but also building India’s grassroots economy and promoting inclusive growth.
| UPSC PYQ |
| Q. Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana is aimed at? (2016)
(a) bringing the small entrepreneurs into formal financial system (b) providing loans to poor farmers for cultivating particular crops (c) providing pensions to old and destitute persons (d) funding the voluntary organisations involved in the promotion of skill development and employment generation Ans: A |


 Free Cash Schemes Boom in India: Finance...
Free Cash Schemes Boom in India: Finance...
 Finance Commission Report 2026 (FC-16): ...
Finance Commission Report 2026 (FC-16): ...
 India–US Trade Deal 2026: Key Features...
India–US Trade Deal 2026: Key Features...

























