Table of Contents
Context: A recent survey reveals that over half of Togolese support leaving ECOWAS to join the Sahel States Alliance.
Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) is a regional political and economic group consisting of fifteen nations in the West African region. Founded in 1975 by the Treaty of Lagos, ECOWAS was formed to spur economic integration, mutual self-sufficiency, and regional stability and peace among the nations. ECOWAS creates free trade, people and goods movement, and balances monetary cooperation in the region.
ECOWAS also has an important role in conflict mediation and peacekeeping operations throughout West Africa through its institutions like the ECOWAS Commission, the Community Court of Justice, and the ECOWAS Parliament. Nigeria, Ghana, Senegal, Côte d’Ivoire, and more are some of its member states with headquarters in Abuja, Nigeria.
| Facts about ECOWAS | |
| Founded | 1975 (Treaty of Lagos) |
| Mission | Foster economic integration among member states |
| Vision | Seamless region with democratic governance, the rule of law, and effective governance |
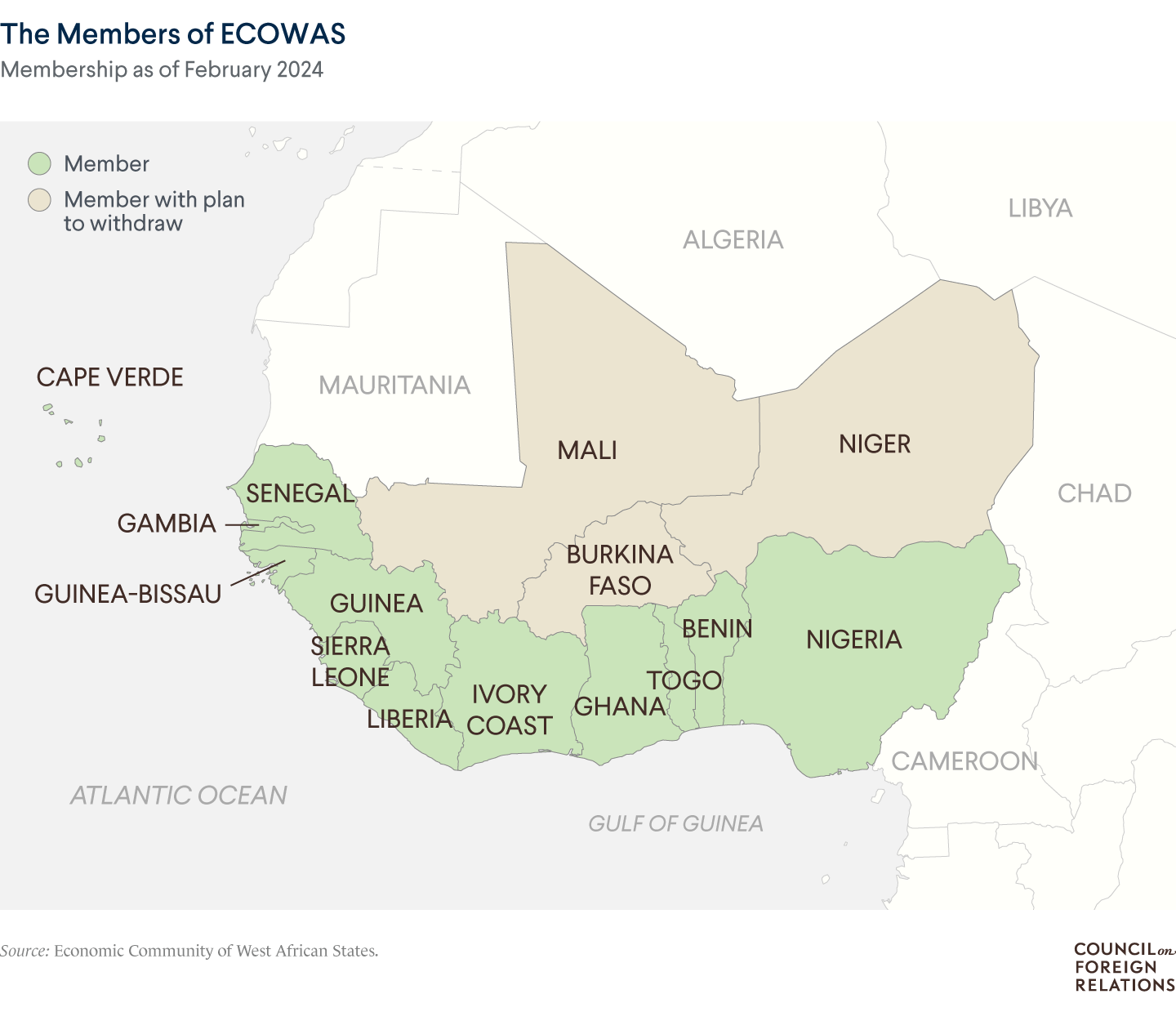
| Members | 12
Mali, Niger, Burkina Faso left ECOWAS and formed the Alliance of Sahel States. |
| Key Objectives |
|
| Conflict Resolution |
|
| Headquarters | Abuja, Nigeria |
50th Anniversary of ECOWAS
ECOWAS observed its 50th anniversary in May 2025, but is going through one of the largest crises in its history because of a series of military coups and resultant withdrawals by major member states.
- Military Coups: Since 2020, Mali, Burkina Faso (2022), and Niger (2023) have suffered military coups, and their membership was suspended from ECOWAS, and sanctions were imposed upon them by the bloc.
- Withdrawal of Three Nations: On 29 January 2025, the military regimes of Mali, Burkina Faso, and Niger officially declared their immediate withdrawal from the ECOWAS membership. They blamed the bloc for not protecting member countries from security threats (such as jihadist violence) and for being controlled by foreign powers (namely France).
- These three countries later created their own security and economic alliance, the Alliance of Sahel States (AES), in September 2024.
- Crisis of Credibility and Unity: These withdrawals have severely bruised ECOWAS’s credibility and its authority, and have raised questions about its future as well as the effectiveness of its democratic and security processes.
- Regional Security: The subregion continues to be bedevilled by insecurity, such as terrorism and transnational organised crime, especially in the Sahel subregion.
- Economic Disparities: Economic imbalance within member states and the failure to create sustainable jobs, particularly for young people, continue to be sources of disillusionment and instability.
| Sahel States |
| The three countries—Mali, Burkina Faso, andNiger—formed the Alliance of Sahel States (AES) to seek military support from Russia while distancing themselves from the influence of the US and France.
The Sahel is a semi-arid region in western and north-central Africa, serving as a transitional zone between the Sahara Desert to the north and the humid savannas to the south. |
Original ECOWAS Countries
ECOWAS was initially comprised of 15 members:
- Benin
- Burkina Faso
- Cabo Verde (Cape Verde)
- Côte d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Liberia
- Mali
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Senegal
- Sierra Leone
- Togo
Purpose of ECOWAS Countries
ECOWAS was created with the vision of making the “borderless region” accessible to the population so that they have access to and benefit from its rich resources through opportunities provided within a sustainable environment. Its overall objectives are:
- Economic Integration: The formation of one large, unified trading bloc through economic integration with a view to a single currency and macroeconomic convergence. This encompasses measures such as the ECOWAS Trade Liberalisation Scheme (ETLS) and moves towards the establishment of a common external tariff.
- Peace and Security: Building a peacekeeping force (ECOMOG – ECOWAS Monitoring Group) to support conflict resolution and peace support operations in the region. It has intervened in Liberia, Sierra Leone, and Guinea-Bissau.
- Social and Cultural Development: Encouraging collaboration in such fields as industry, transportation, telecommunications, energy, agriculture, natural resources, trade, monetary and financial affairs, and social and cultural issues.
- Democracy and Good Governance: Encouraging compliance with democratic principles, the rule of law, and good governance among members.


 United Nations General Assembly (UNGA), ...
United Nations General Assembly (UNGA), ...
 Universal Postal Union (UPU), Objective,...
Universal Postal Union (UPU), Objective,...
 World Meteorological Organisation (WMO),...
World Meteorological Organisation (WMO),...

























