Table of Contents
Protecting Red Sea Shipping
Context:
- Despite theS.-led Operation Prosperity Guardian to protect commercial traffic through the Red Sea, shippers have warned that the Houthi factor could compel the use of longer routes for several more months.
- The European Union also launched a naval mission to protect Red Sea shipping from Yemen’s Houthi rebels as a U.S.-owned cargo vessel repeatedly came under fire in the region.
About Operation Prosperity Guardian
- Goal: Counter Houthi attacks on merchant ships in the southern Red Sea.
- Led by: US, under the Combined Task Force 153 (CTF 153).
- Reason for escalation: Houthi attacks initially targeted ships supporting Hamas, but have expanded to include all merchant tankers in the Bab el-Mandeb strait.
- Participants:
- US: Three destroyers
- UK: HMS Diamond
| EU Red Sea Mission |
|
- Potential impact:
- Increased security for merchant ships in the region.
- Deterrence of future Houthi attacks.
- Potential for longer shipping routes due to continued Houthi activity.
- Increased shipping costs for exporters.
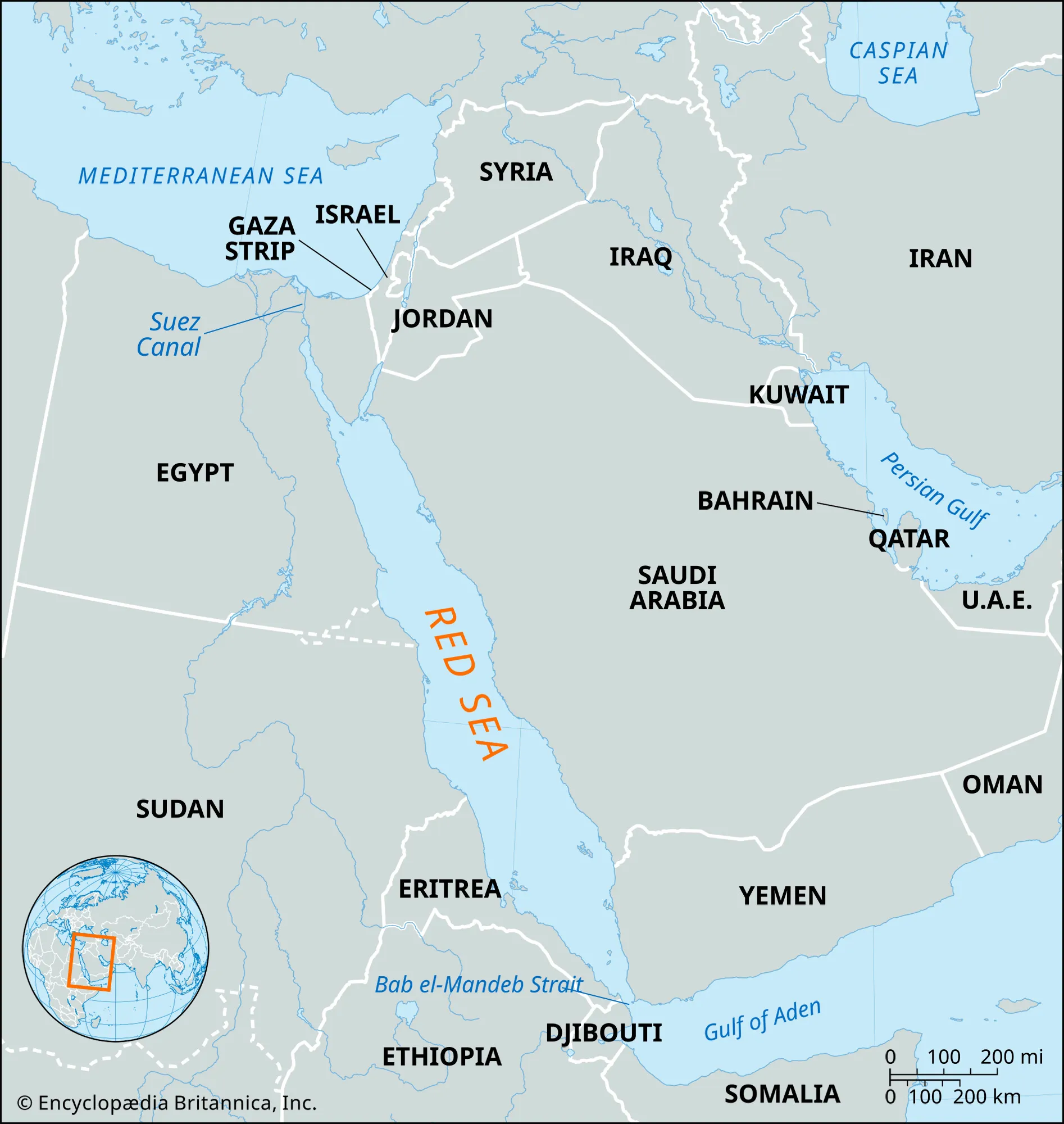
What are the Ongoing Issues?
Disruptions to global shipping caused by Houthi attacks:
- The Houthi rebels in Yemen have been launching attacks on ships in the Red Sea since November 2023, targeting both commercial and military vessels.
- This has caused disruptions to global shipping lanes, as the Red Sea is a crucial waterway for trade between Asia, Europe, and Africa.
- For instance, the Red Sea region is critical for 30% of global container traffic and 12% of global trade.
- This could have ripple effects on other countries that rely on trade through the Red Sea.
Heightened geopolitical tensions in the region:
- The Houthi attacks are part of a wider conflict in Yemen, which has been ongoing since 2015.
- The recent escalation in attacks is linked to the ongoing war in Gaza between Israel and Hamas, with the Houthis claiming their actions are in support of the Palestinians.
- This has increased tensions between Iran (which backs the Houthis) and Saudi Arabia (which leads a coalition supporting the Yemeni government).
- The involvement of regional and international powers raises concerns about a wider conflict erupting in the already volatile Middle East.
We’re now on WhatsApp. Click to Join
Northern Ireland– Political Deadlock
Context: After a pause in cooperation following the 2022 elections, the two leading parties in Northern Ireland have now formed a new government.
Background: Brexit and Northern Ireland’s Dilemma
- Brexit Referendum: In 2016, the U.K. voted to leave the EU, triggering complex negotiations due to Northern Ireland (NI) sharing a border with EU member Ireland.
- Good Friday Agreement: The 1998 agreement brought peace to NI and required the maintenance of an open border between Northern Ireland and Ireland.
- 2016 Aftermath: The U.K.’s decision to leave the EU necessitated a new approach to the NI border to preserve the Good Friday Agreement and the EU’s single market.
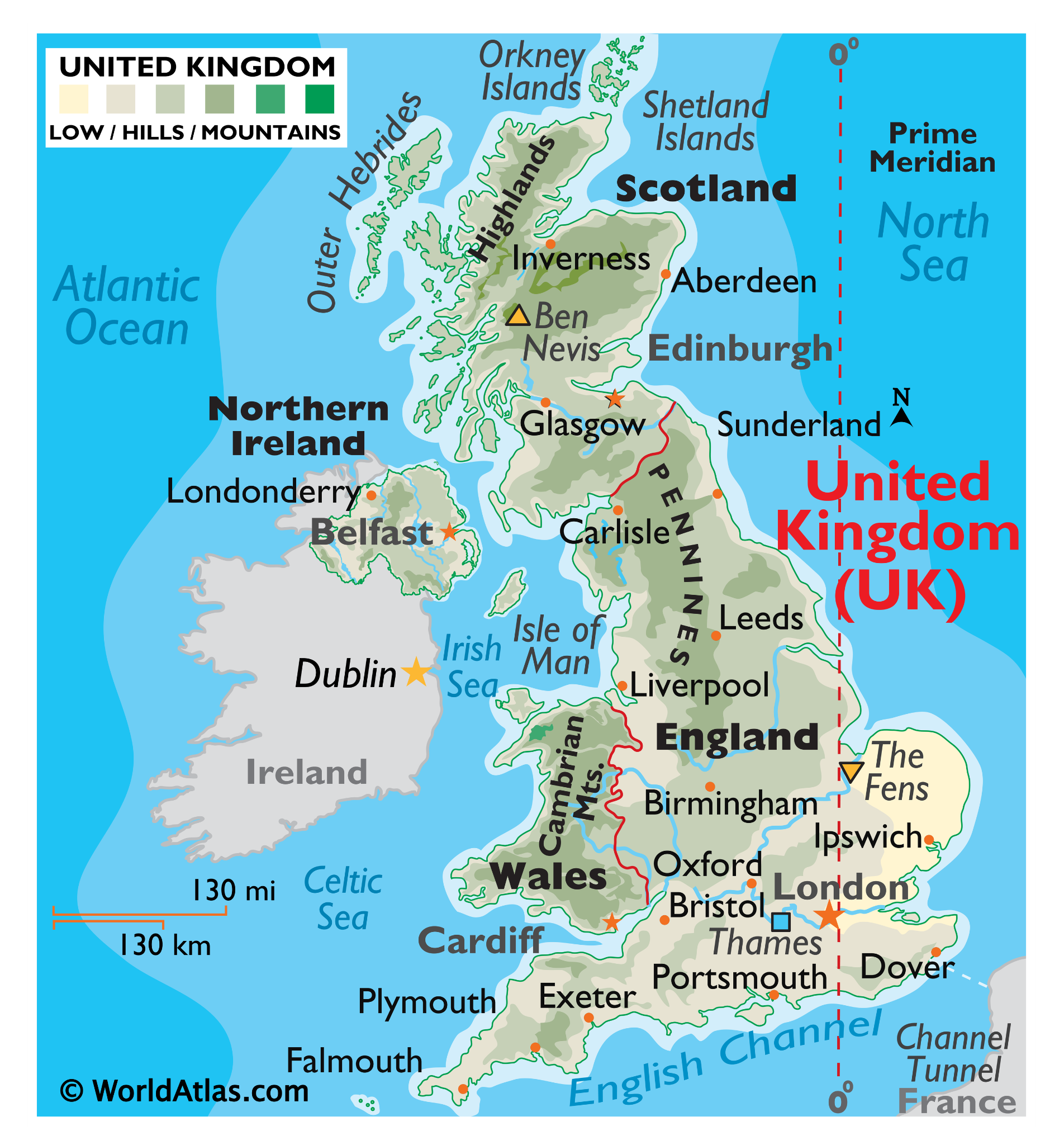
The DUP’s Boycott and Political Stalemate
- 2020 Withdrawal Agreement: The Democratic Unionist Party (DUP) supported the U.K. government’s withdrawal but opposed the resulting trade border in the Irish Sea.
- 2022 Stormont Elections: The DUP boycotted the government formation following the elections due to the trade border issue.
Deals Made to Address Trade and Governance
- Windsor Framework: Introduced in 2023 to simplify trade between NI and Great Britain, distinguishing between goods staying in the U.K. and those going to the EU.
- Command Paper Proposal: Eased trade procedures further by exempting 80% of goods from checks and creating an oversight body for NI’s market status.
Outcomes and Government Formation
- Sinn Fein’s Victory: Sinn Fein won the most seats in the 2022 elections, advocating for Irish unity and signalling a shift in NI’s political landscape.
- First Nationalist Prime Minister: Michelle O’Neill of Sinn Fein became NI’s first nationalist Prime Minister, with the DUP’s Emma Little-Pengelly as deputy.
- DUP’s Return to Governance: Amidst economic pressures and demographic changes, the DUP returned to the government, needing to address the new realities.
| What Is Windsor Framework? |
| The ‘Windsor Framework’ replaced the Northern Ireland Protocol.
Key Aspects Of the Framework
Northern Ireland Protocol
|
Privilege Committee of Lok Sabha
Context: The Supreme Court halted the summons of the West Bengal Chief Secretary and other officers by a Lok Sabha Privilege committee investigating a BJP MP’s complaint of mistreatment.
About the Privilege Committee
- Composition: The Lok Sabha’s Privileges Committee has 15 members nominated by the Speaker.
| For Rajya Sabha |
|
- Function: It investigates breaches of privilege of the House or its members upon referral.
- Process:
- Members can raise privilege questions with the Speaker’s consent.
- The committee examines cases, hears testimonies, and reviews evidence.
- There is no deadline for the committee to issue its report.
- Recommendations: The committee makes recommendations at its discretion after review.
- Punishments:
- The respective Houses of Parliament decide on punishments.
- Penalties can include suspension or expulsion from the House.
- Past Incidents:
- In 2005, 11 MPs were expelled for a cash-for-query scandal.
- In 1978, Indira Gandhi was expelled following the Justice Shah Commission’s Emergency abuses report.
| Parliamentary Privilege |
|
Use of AI in Scientific Discoveries and Healthcare
Context: The iOncology AI initiative, leveraging a supercomputer in Pune and the Charak I server at the National Cancer Institute campus in Jhajjar, represents a significant advancement in the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare and scientific discovery.
About iOncology AI Project
- Goal: Develop an AI-powered platform (iOncology AI) to help oncologists select the most effective treatment for cancer patients based on their genetic makeup.
Key Features:
- Data Collection: Stores patients’ blood tests, lab reports, scans, and medical history.
- Accuracy: Trained on 1,500 breast and ovarian cancer cases, achieving 75% accuracy compared to clinician diagnosis.
- Focus Cancers: Currently trained for breast and ovarian cancers, expanding to head and neck, colorectal, and blood cancers.
- Confidentiality: Maintains patient privacy through individual logins and anonymized data analysis.
Significance:
- Improved Treatment Selection: Provides data-driven insights to guide oncologists in choosing the best treatment for each patient.
- Personalised Medicine: Advances personalised medicine by considering individual genetic variations for targeted therapy.
- Early Detection Potential: May contribute to earlier cancer detection through AI-assisted analysis of scans and reports.
- Resource Optimization: Offers potential for effective treatment in resource-limited settings.
- Data-Driven Research: Generates valuable data for developing prevention strategies and treatment protocols specific to the Indian population.
Future Scope:
- Expand AI models to cover more cancer types and treatment modalities.
- Integrate epigenetic data to understand how genes are regulated, further personalising treatment.
- Validate and implement the platform in wider clinical settings.
| AlphaFold 2 |
|
AI Cameras to monitor Elephants
Context: The Forest department has installed an artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled surveillance camera system at Anakkulam, under the Mankulam forest division in Idukki, to provide imagery of herds of wild elephants.
More In News
- The Mankulam forest division has implemented the project in association with the Government Engineering College, Idukki.
- The Mankulam forest division is one of the UNESCO World Heritage Sites in the Western Ghats in the State.


 Graphic Processing Units (GPUs) – Work...
Graphic Processing Units (GPUs) – Work...
 Gold Imports and the Indian Economy – ...
Gold Imports and the Indian Economy – ...
 Nilgiri Tahr Conservation: Ecology, Habi...
Nilgiri Tahr Conservation: Ecology, Habi...




















